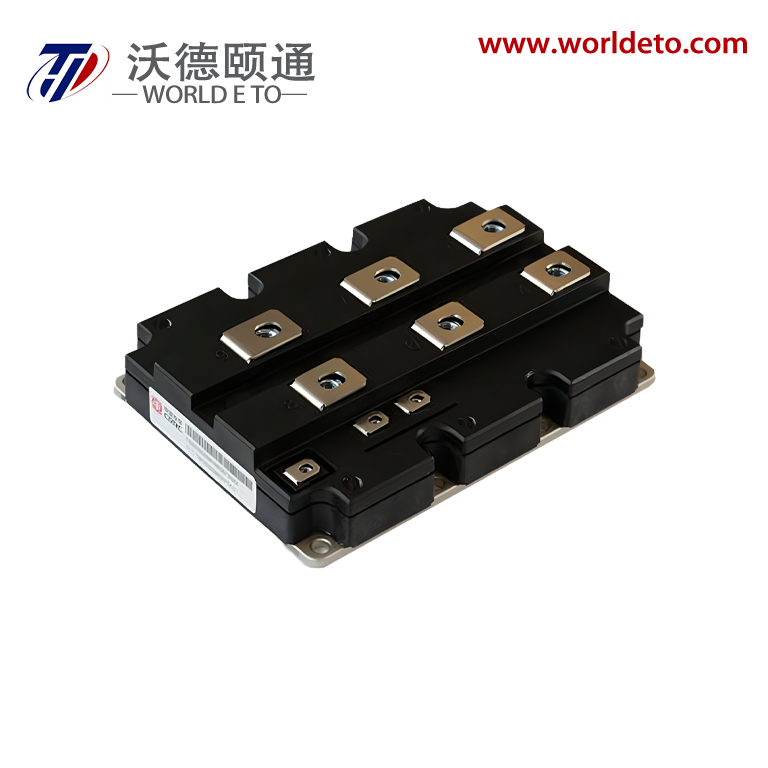
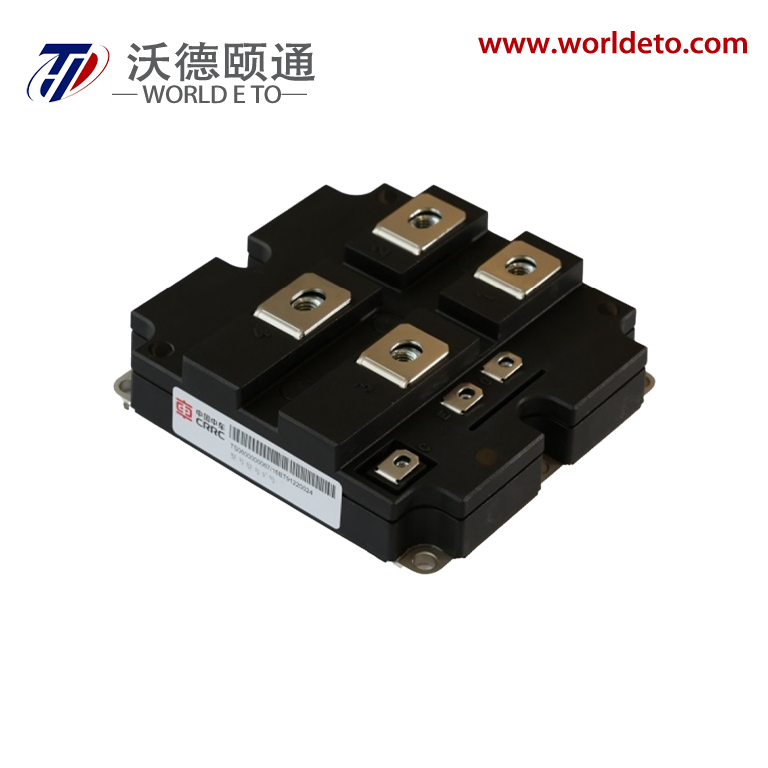
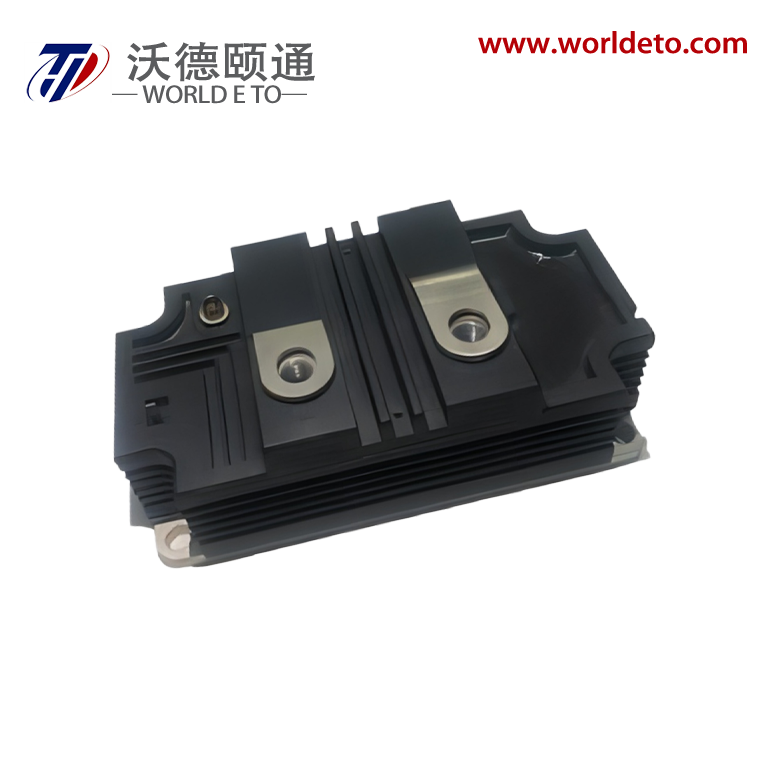
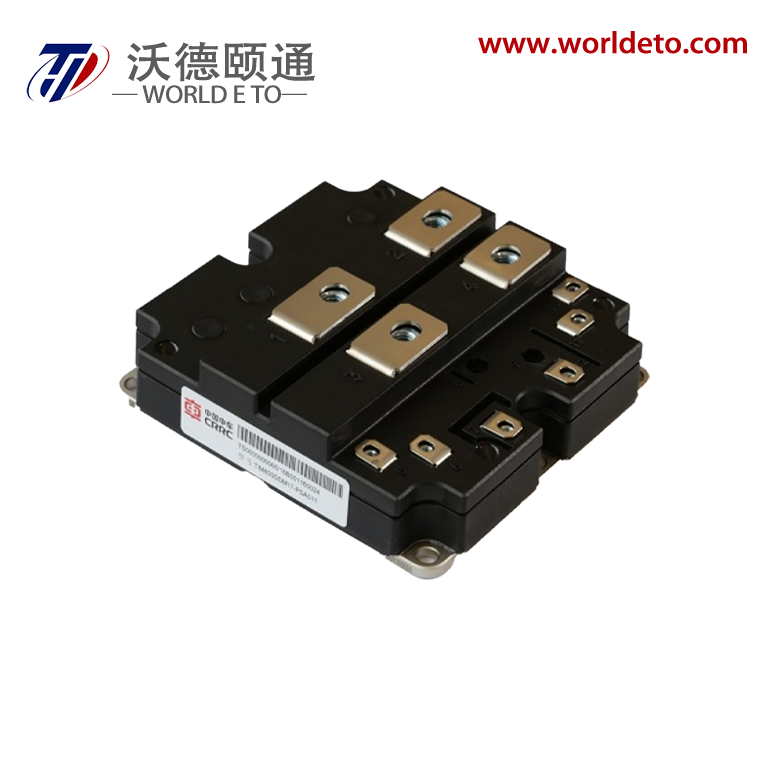
thyristor transistor
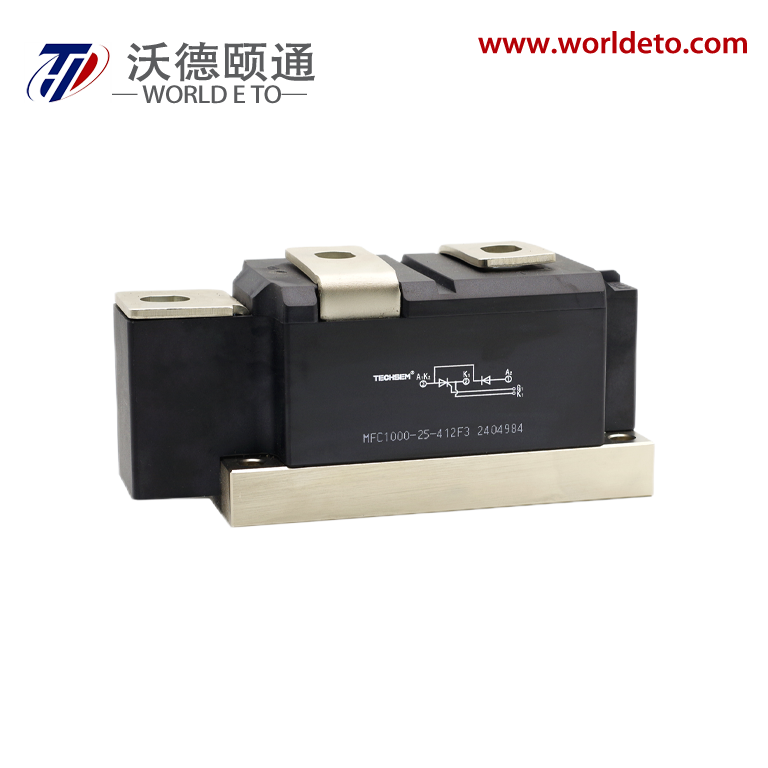
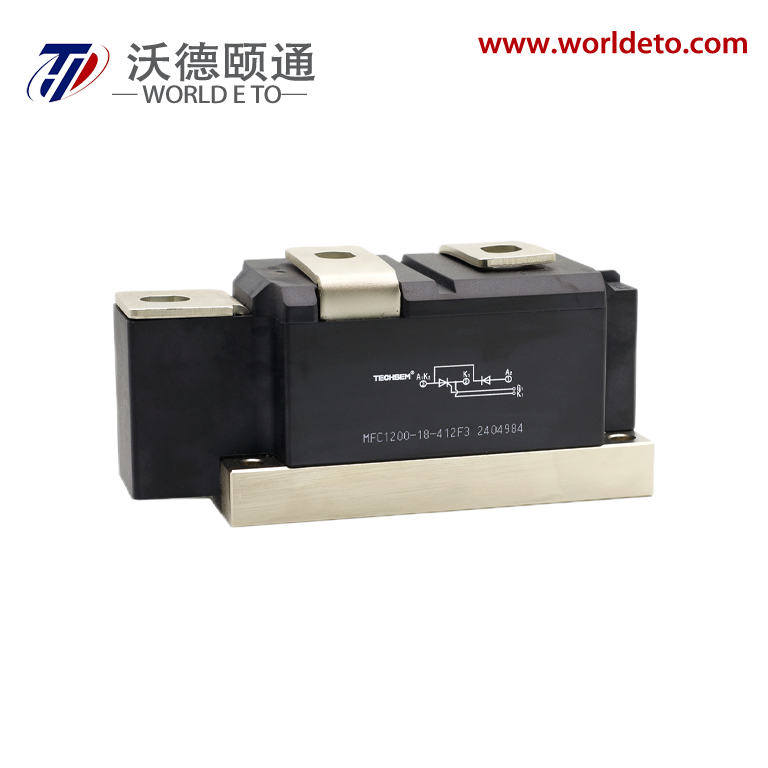
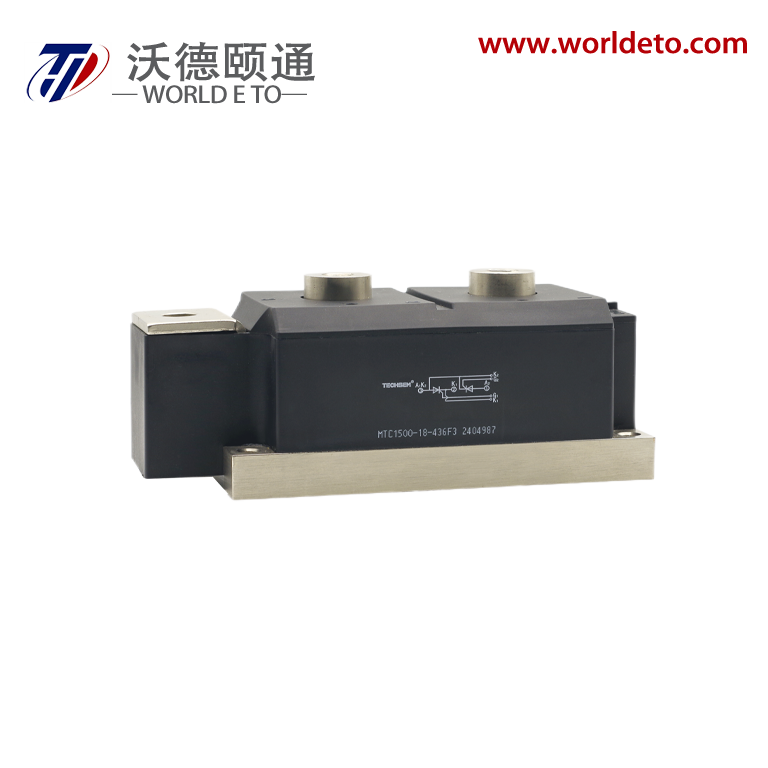
The thyristor transistor represents a groundbreaking semiconductor device that combines the switching capabilities of traditional transistors with the power-handling characteristics of thyristors. This innovative component operates as a four-layer semiconductor structure, typically composed of alternating P-type and N-type silicon materials arranged in a PNPN configuration. The thyristor transistor functions as a controlled rectifier, allowing current to flow in one direction while providing precise control over the switching process through gate terminal manipulation. Unlike conventional transistors that require continuous base current for operation, the thyristor transistor maintains its conductive state once triggered, making it exceptionally efficient for high-power applications. The device incorporates three primary terminals: anode, cathode, and gate, each serving distinct roles in the switching mechanism. When a positive voltage pulse is applied to the gate terminal, the thyristor transistor transitions from its blocking state to conducting state, allowing substantial current to pass through the main circuit. This switching characteristic enables the device to handle voltages ranging from hundreds to thousands of volts while managing currents from amperes to kiloamperes. The technological architecture of the thyristor transistor utilizes regenerative feedback within its four-layer structure, creating a bistable switching behavior that distinguishes it from linear amplification devices. Modern manufacturing processes employ advanced doping techniques and precision fabrication methods to optimize the device's switching speed, voltage rating, and thermal performance. The thyristor transistor finds extensive applications across industrial automation systems, motor control circuits, power conversion equipment, and lighting control systems. Its ability to efficiently switch high-power loads makes it indispensable in AC motor drives, welding equipment, battery chargers, and renewable energy systems. The device's robust construction and reliable performance characteristics have established it as a preferred choice for demanding industrial environments where conventional switching components might fail under extreme electrical stress conditions.