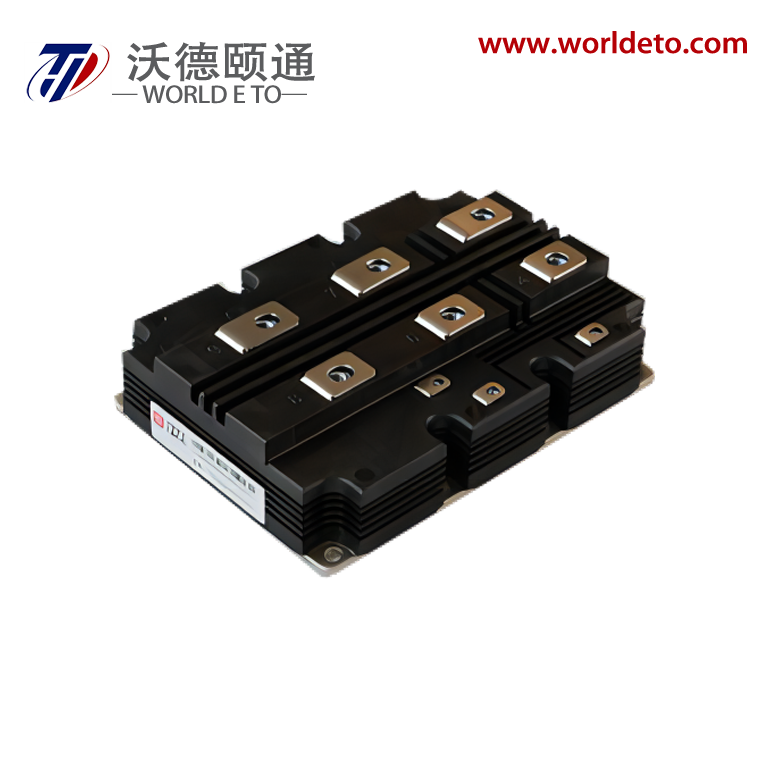
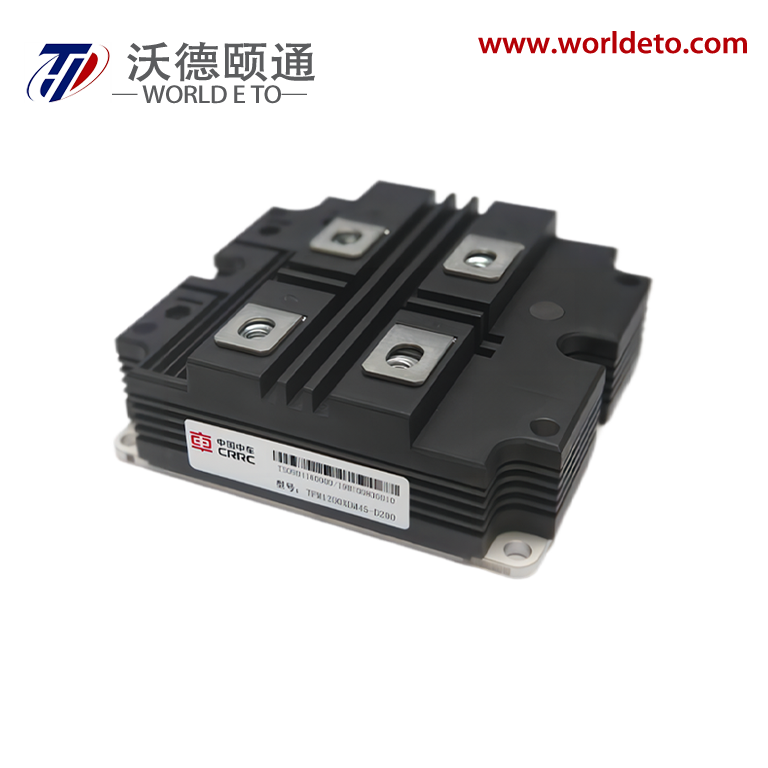
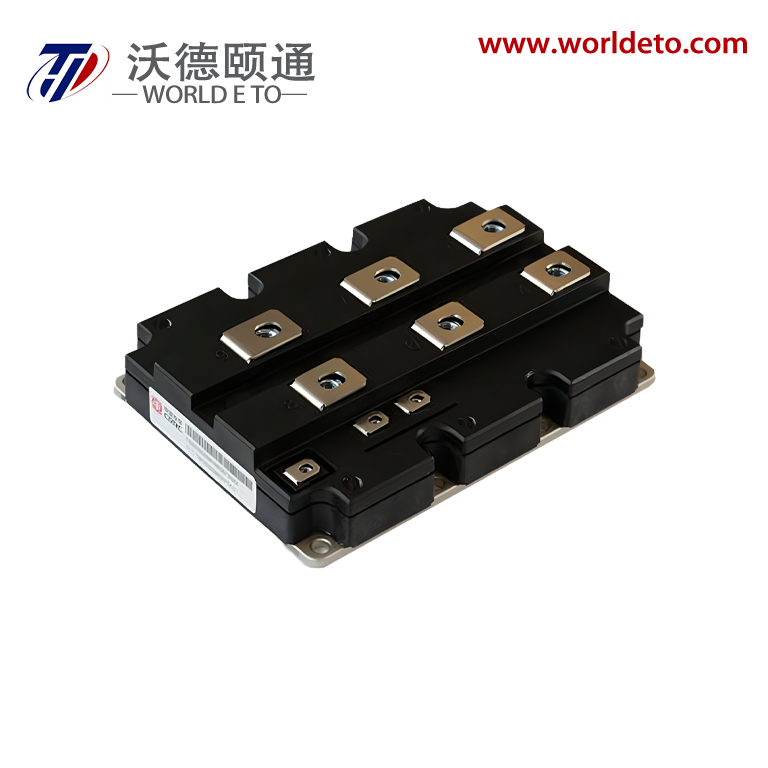
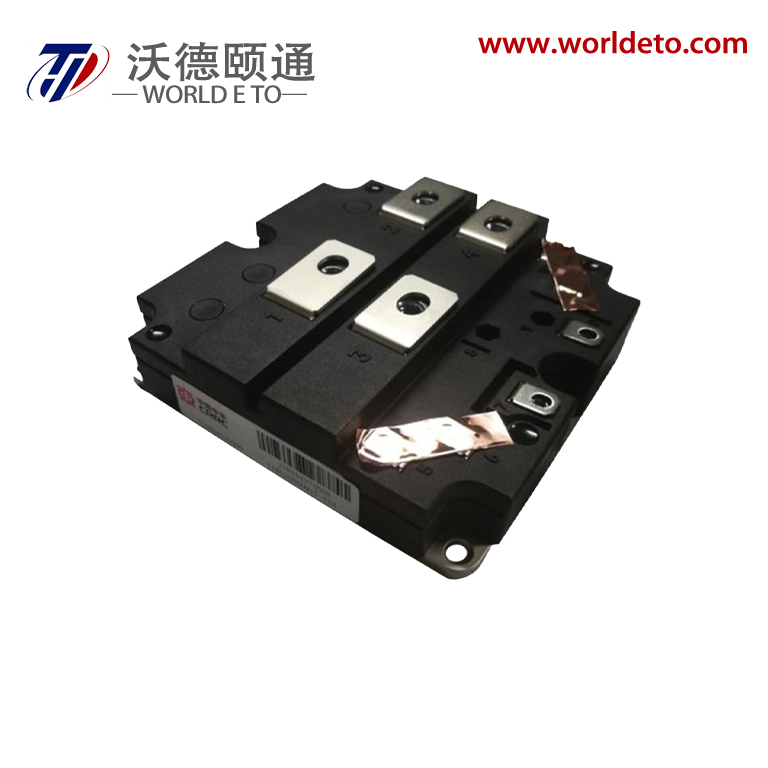
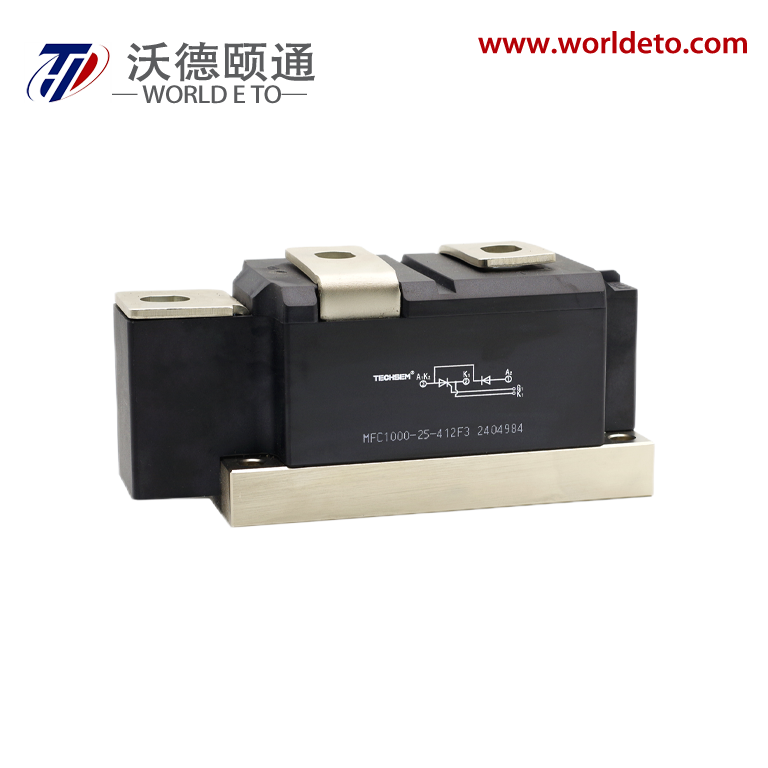
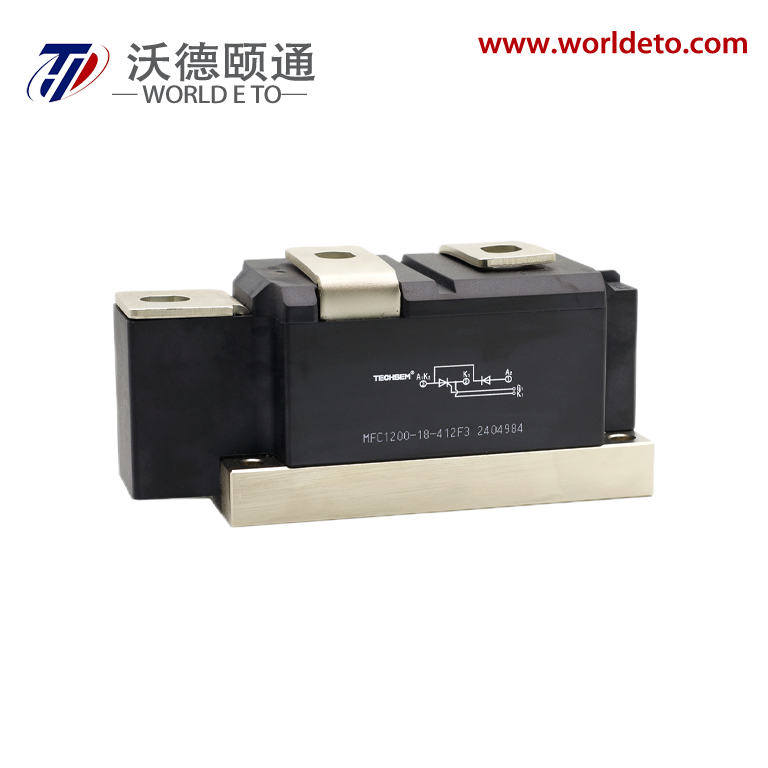
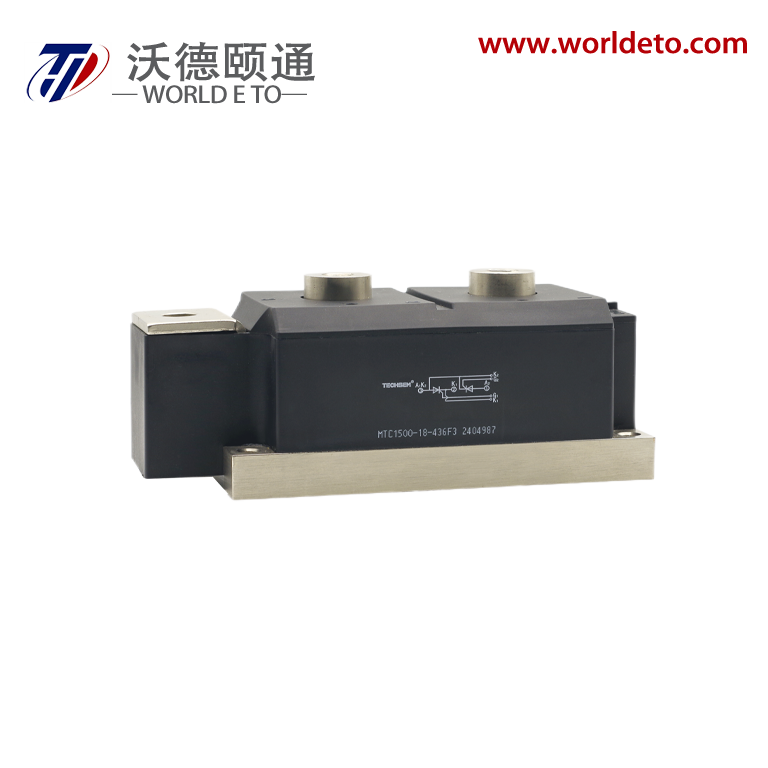
semiconductor transistor
The semiconductor transistor represents one of the most revolutionary innovations in modern electronics, fundamentally transforming how we control and amplify electrical signals. This essential electronic component operates by using semiconductor materials, typically silicon or germanium, to regulate current flow between two terminals through the manipulation of a third control terminal. The semiconductor transistor functions as both a switch and an amplifier, making it indispensable in virtually every electronic device we encounter today. At its core, the semiconductor transistor consists of three layers of semiconductor material arranged in either NPN or PNP configurations, creating two PN junctions that enable precise control over electrical current. The main functions of a semiconductor transistor include signal amplification, where small input signals generate larger output signals, and digital switching, where the device rapidly transitions between on and off states. These capabilities make the semiconductor transistor perfect for applications ranging from simple audio amplifiers to complex computer processors. Technologically, the semiconductor transistor operates on the principle of controlling current flow through the manipulation of charge carriers within the semiconductor material. When a small voltage applies to the base terminal, it controls a much larger current flowing between the collector and emitter terminals. This control mechanism enables the semiconductor transistor to achieve remarkable precision in signal processing applications. Modern semiconductor transistor technology has evolved to include various specialized types such as bipolar junction transistors, field-effect transistors, and metal-oxide-semiconductor transistors, each optimized for specific performance characteristics. The applications of semiconductor transistor technology span across numerous industries, from consumer electronics like smartphones and televisions to industrial automation systems and medical devices. In computing applications, billions of microscopic semiconductor transistor units work together to process information at incredible speeds, enabling everything from basic calculations to artificial intelligence processing.