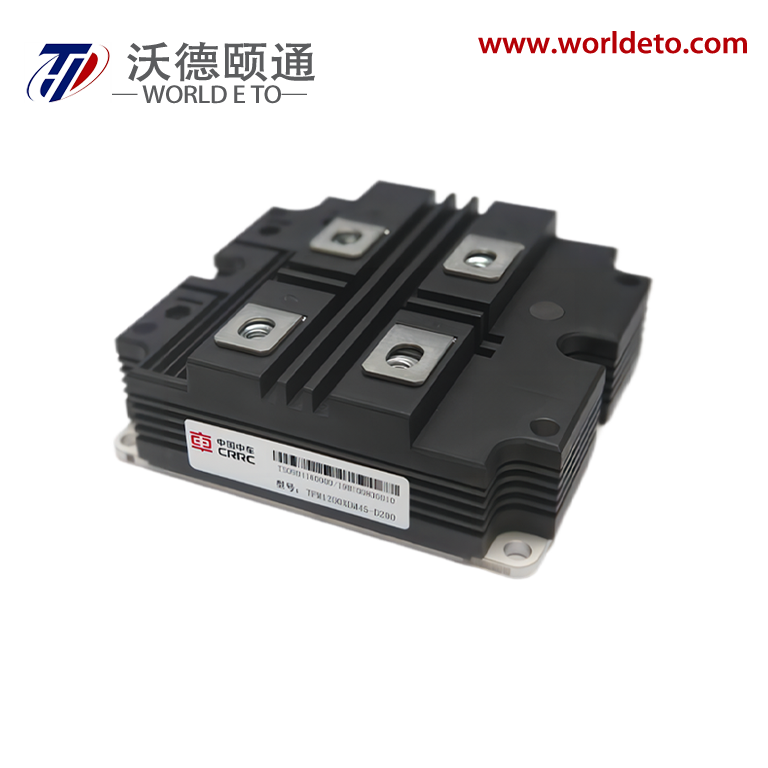
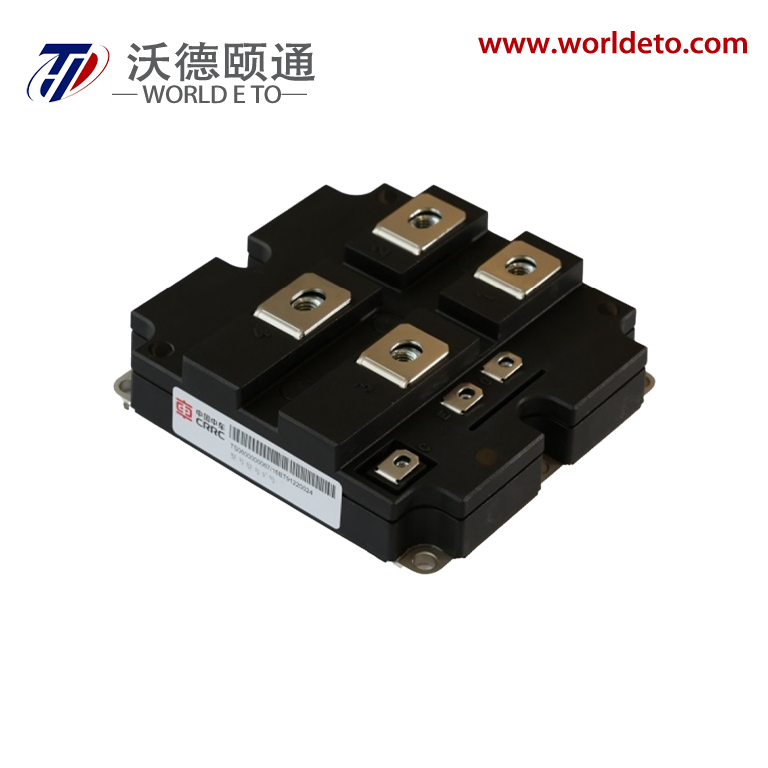
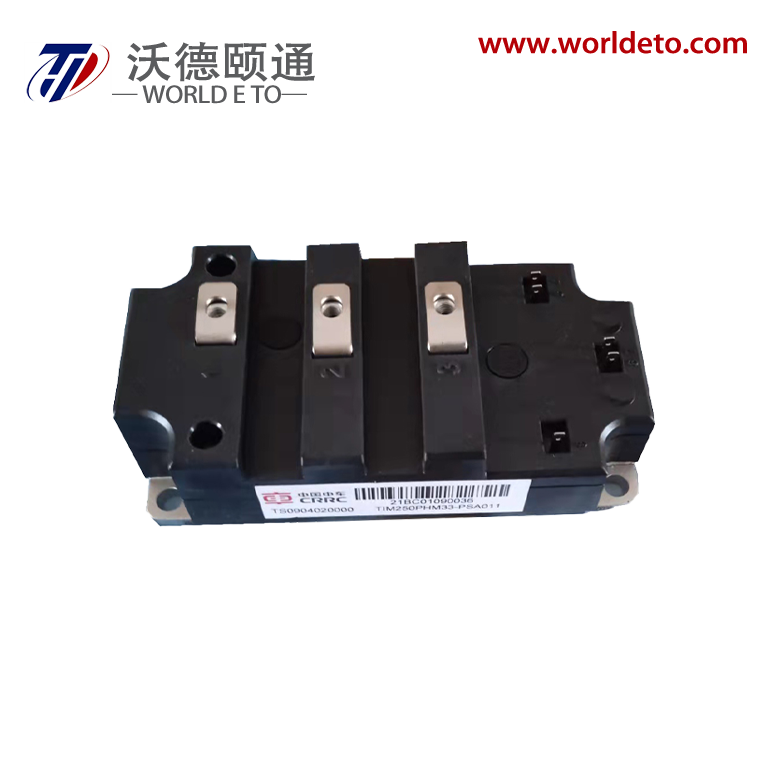
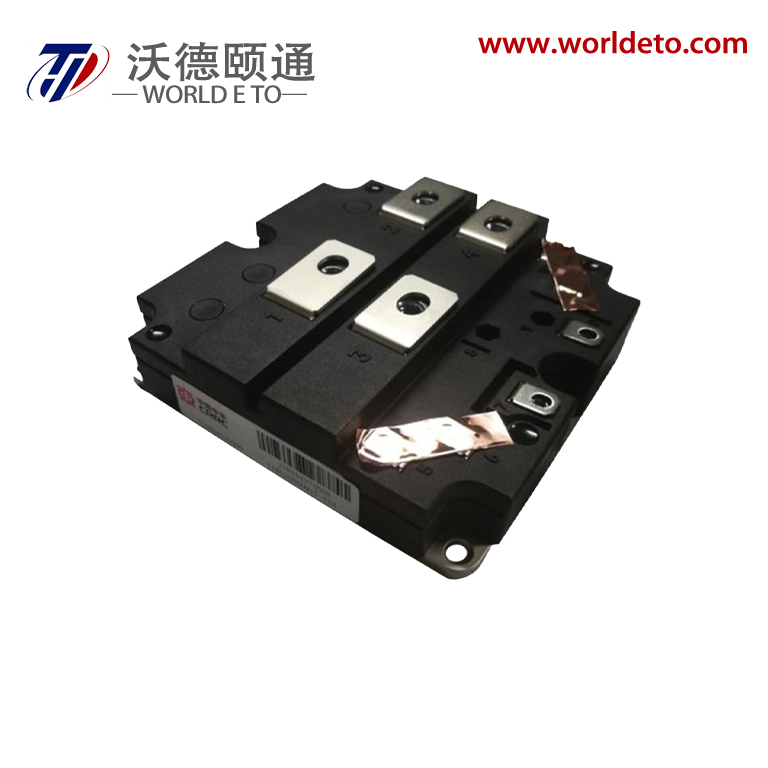
Superior Voltage Regulation and Low Ripple Performance
The bridge type rectifier delivers exceptional voltage regulation and minimal ripple characteristics that establish new standards for power quality in DC applications. This advanced performance stems from the bridge type rectifier's fundamental operating principle, which processes both halves of the AC input waveform to create a more consistent and stable DC output. The mathematical relationship governing bridge type rectifier ripple factor achieves approximately 0.48, representing a dramatic improvement over half-wave rectifiers that produce ripple factors of 1.21. This substantial reduction in ripple content means the bridge type rectifier output contains significantly fewer voltage variations, creating cleaner power that sensitive electronic components require for optimal operation. The superior voltage regulation capabilities of the bridge type rectifier manifest through its ability to maintain consistent output voltages despite variations in input voltage or load current. When AC line voltages fluctuate due to grid conditions or when load demands change during operation, the bridge type rectifier automatically compensates through its inherent design characteristics. This regulation stability proves crucial for applications requiring precise voltage control, such as precision measurement instruments, medical equipment, and computer systems where voltage variations can cause data corruption or component damage. The low ripple performance of the bridge type rectifier reduces filtering requirements downstream, allowing engineers to use smaller capacitors and inductors in their power supply designs. This component reduction translates into cost savings, space savings, and improved reliability as fewer components mean fewer potential failure points. Laboratory measurements consistently demonstrate that bridge type rectifier systems require approximately sixty percent less filtering capacitance compared to half-wave alternatives to achieve equivalent ripple specifications. The practical implications extend to electromagnetic compatibility performance, as the bridge type rectifier's smooth output characteristics generate less electromagnetic interference that could affect nearby sensitive circuits. Audio equipment benefits particularly from the bridge type rectifier's low-noise characteristics, delivering cleaner power that preserves signal integrity and reduces audible distortion. Industrial control systems experience improved accuracy and stability when powered by bridge type rectifier circuits, as the consistent voltage supply enables more precise sensor readings and actuator control. The longevity benefits cannot be overlooked, as electronic components subjected to the stable power delivery of bridge type rectifier systems experience reduced stress and extended operational lifespans.