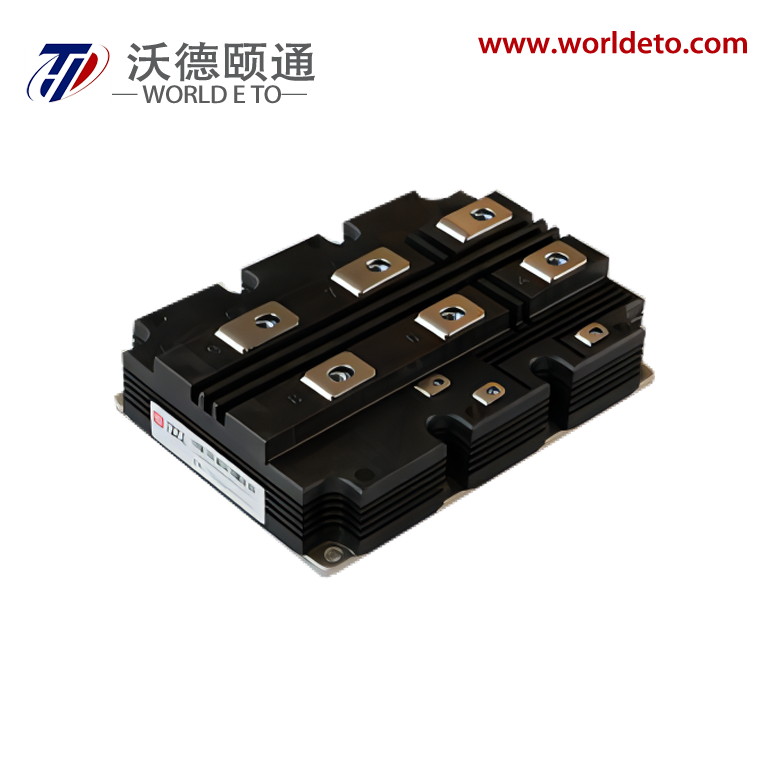
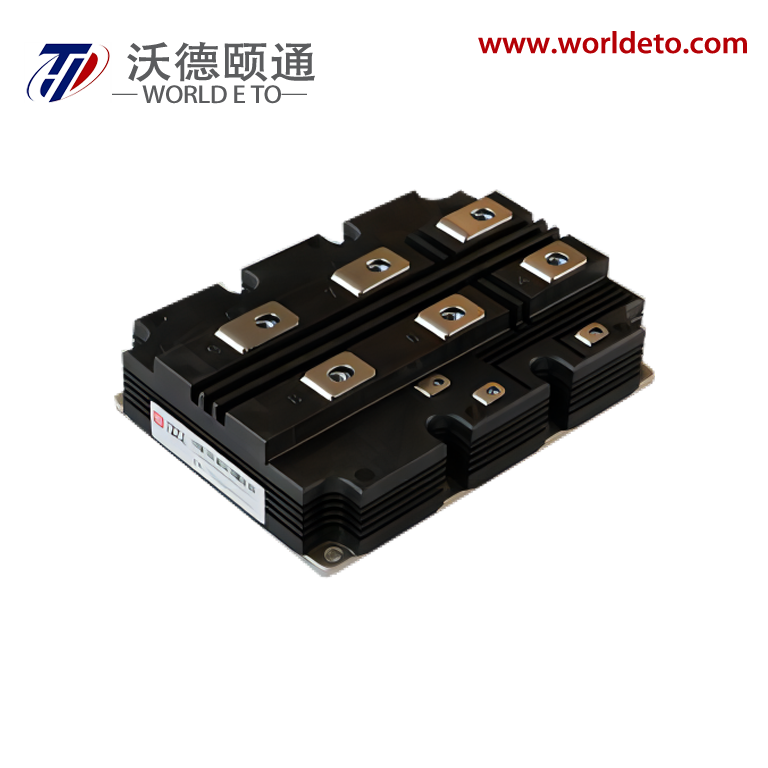
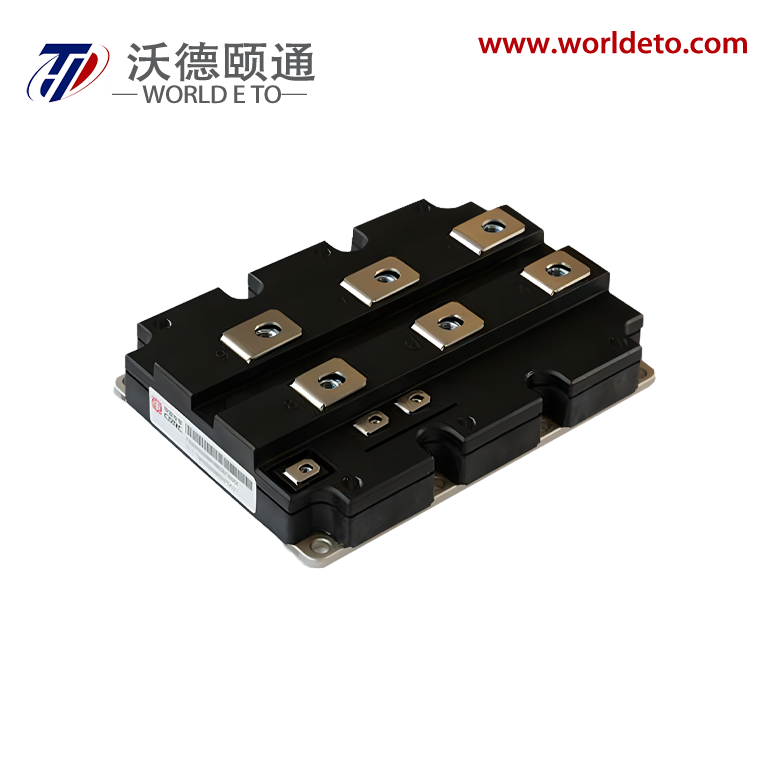
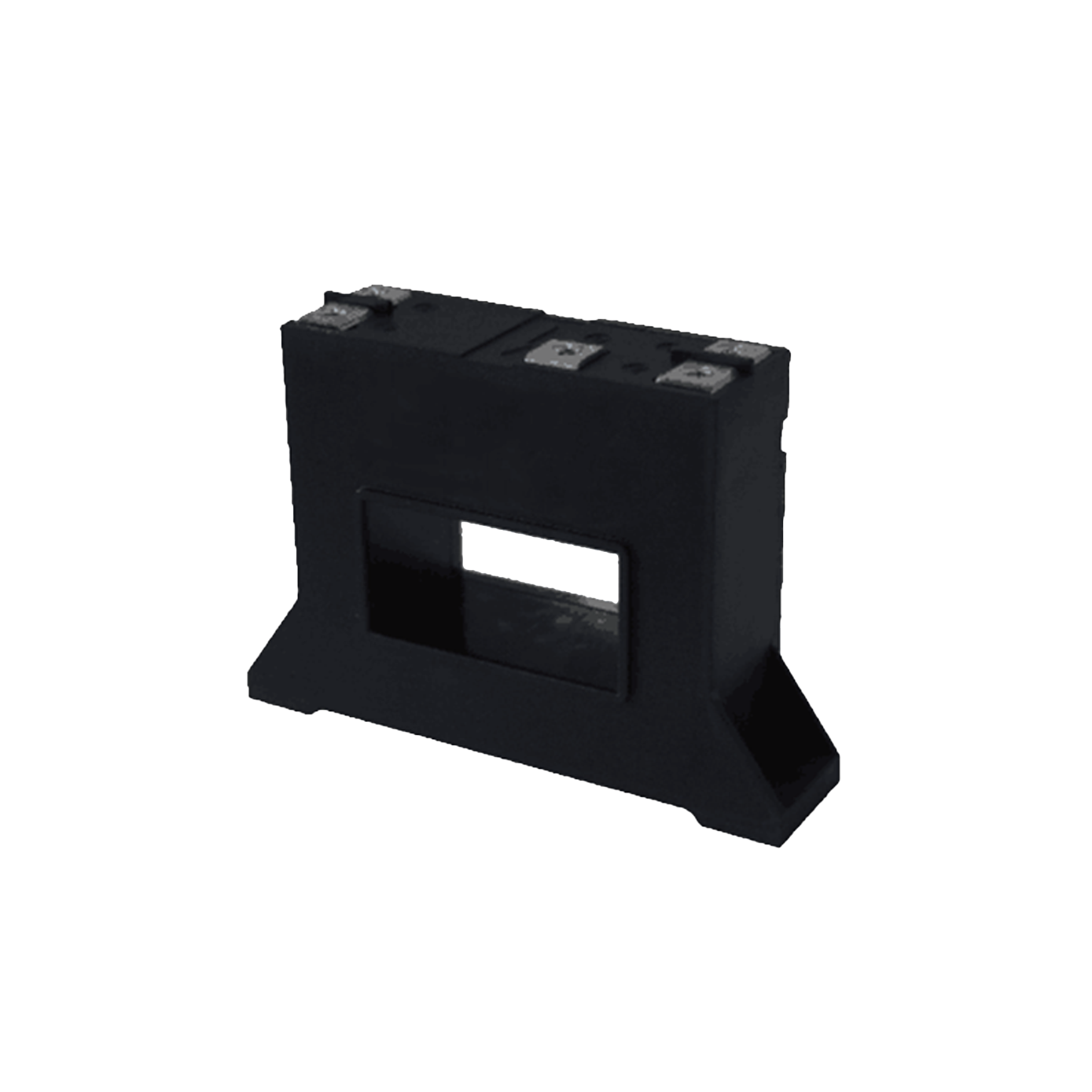
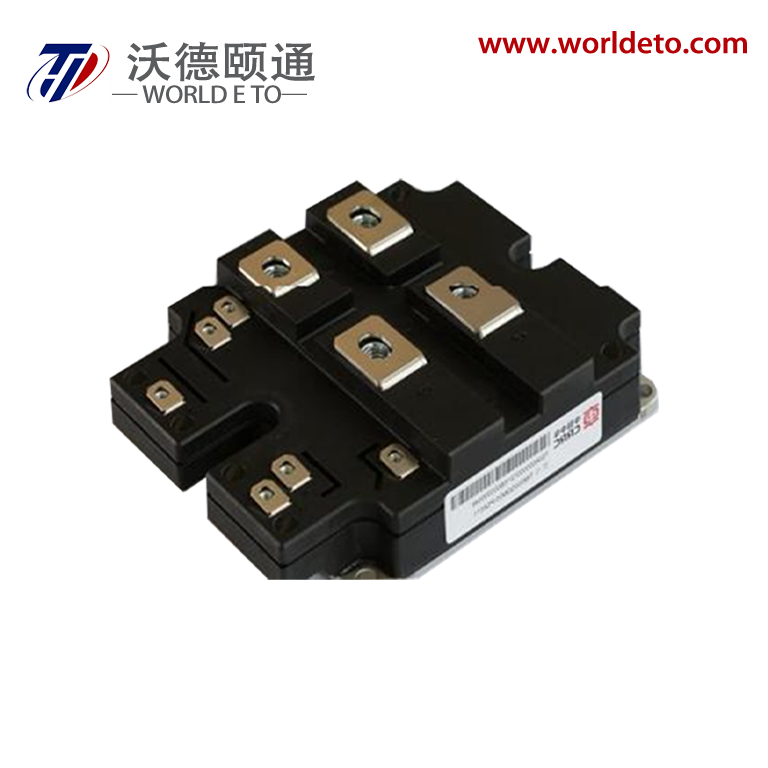
high power rectifier
A high power rectifier is an essential electronic device designed to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) while handling substantial electrical loads efficiently. These sophisticated devices serve as the backbone of numerous industrial and commercial applications where reliable, high-capacity power conversion is critical. The primary function of a high power rectifier involves transforming incoming AC voltage from power grids or generators into stable DC output suitable for powering various equipment and systems. Modern high power rectifier units incorporate advanced semiconductor technology, utilizing silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCR), insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBT), or metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFET) to achieve superior performance characteristics. These technological features enable precise control over output voltage and current parameters while maintaining exceptional efficiency levels typically exceeding 95 percent. The rectification process occurs through controlled switching mechanisms that allow current flow in one direction only, effectively eliminating the alternating characteristics of input power. Contemporary high power rectifier designs integrate sophisticated control systems featuring microprocessor-based regulation, digital display interfaces, and comprehensive protection circuits. These protection mechanisms safeguard against overcurrent, overvoltage, overheating, and short-circuit conditions, ensuring reliable operation even under demanding conditions. Applications for high power rectifier systems span across electroplating facilities, metal refining operations, battery charging stations, telecommunications infrastructure, data centers, renewable energy installations, electric vehicle charging networks, and industrial motor drives. The robust construction of these units typically includes heavy-duty heat sinks, forced air or liquid cooling systems, and reinforced enclosures designed to withstand harsh industrial environments while maintaining optimal performance standards throughout extended operational periods.