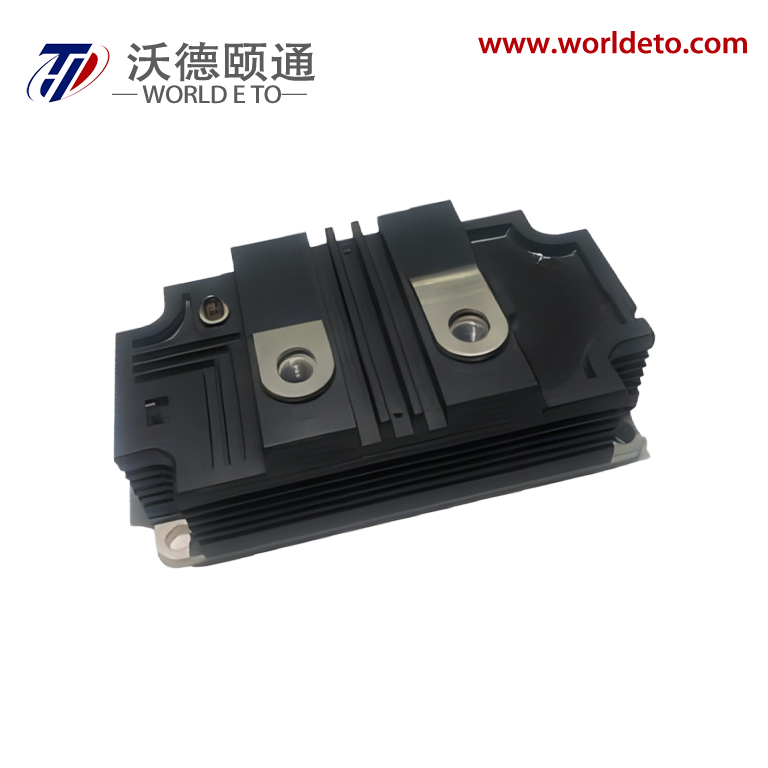
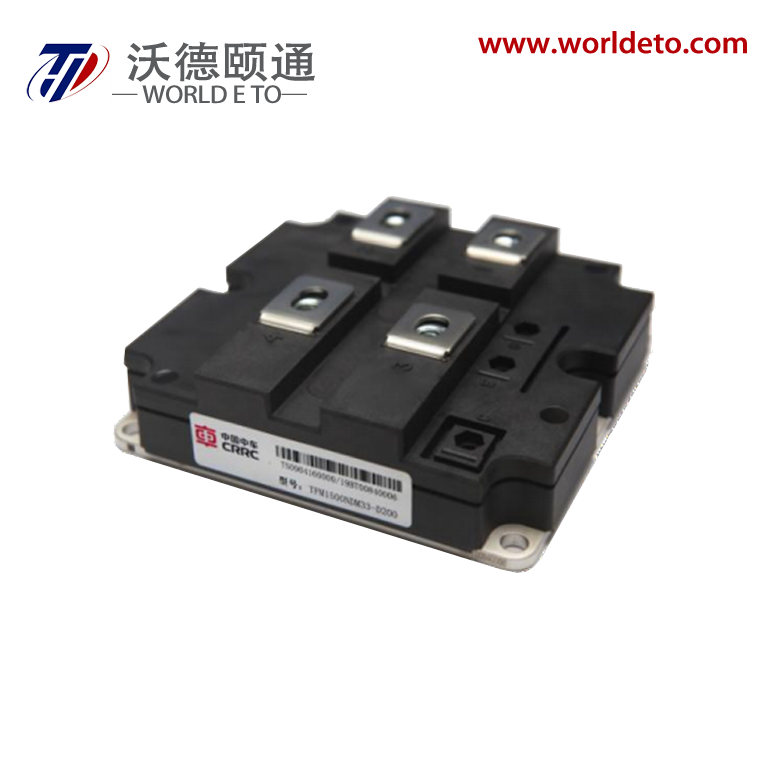
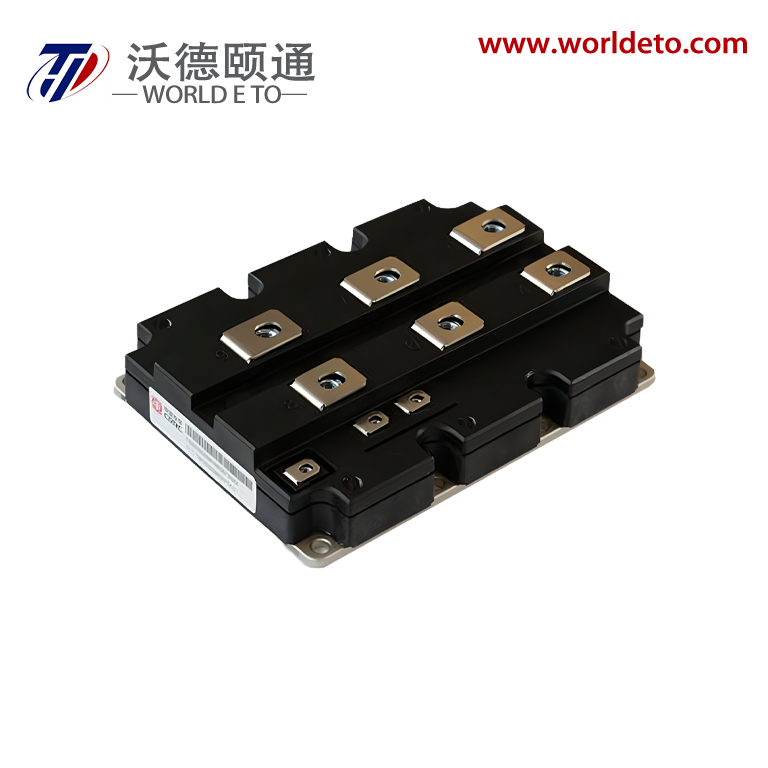
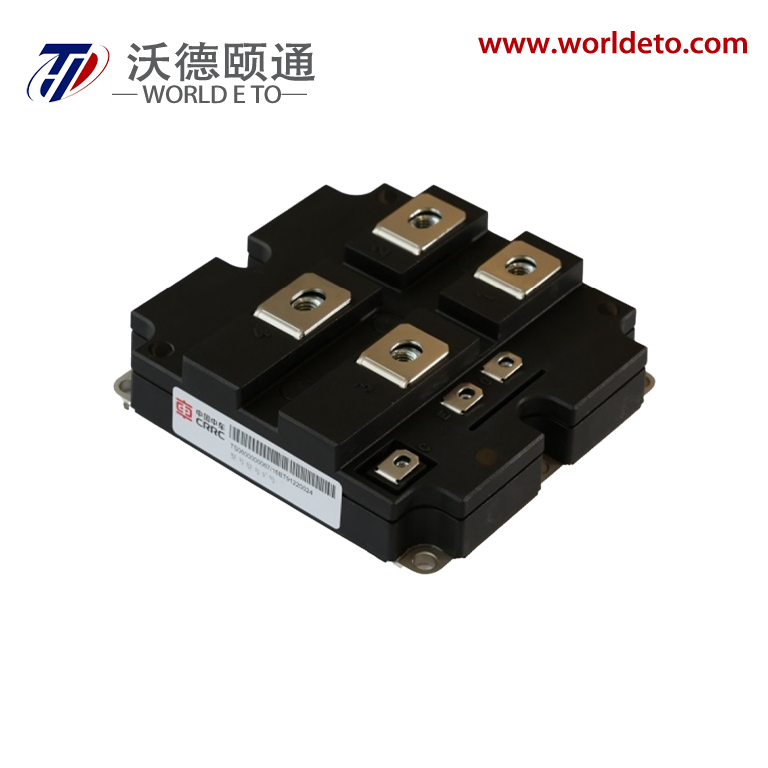
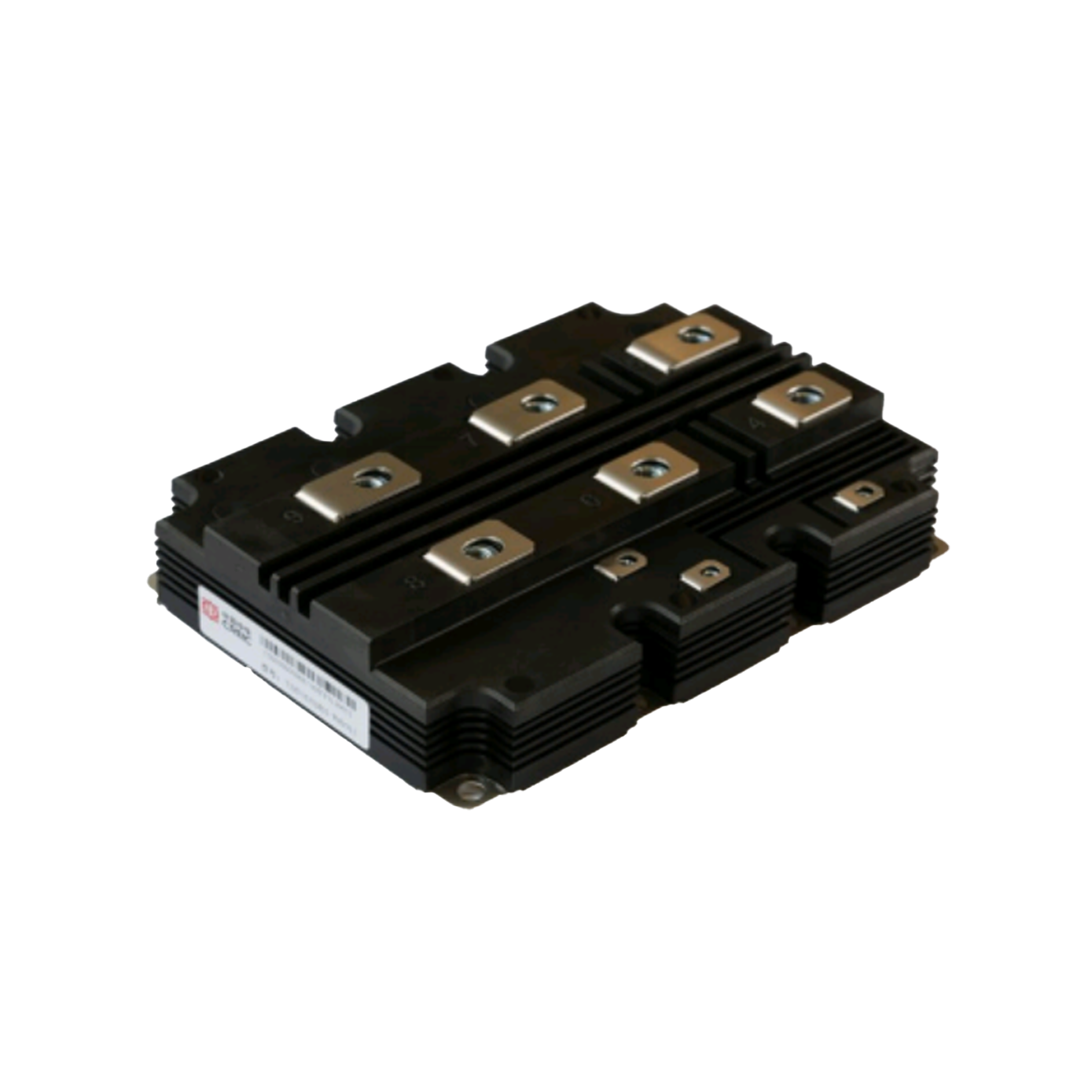
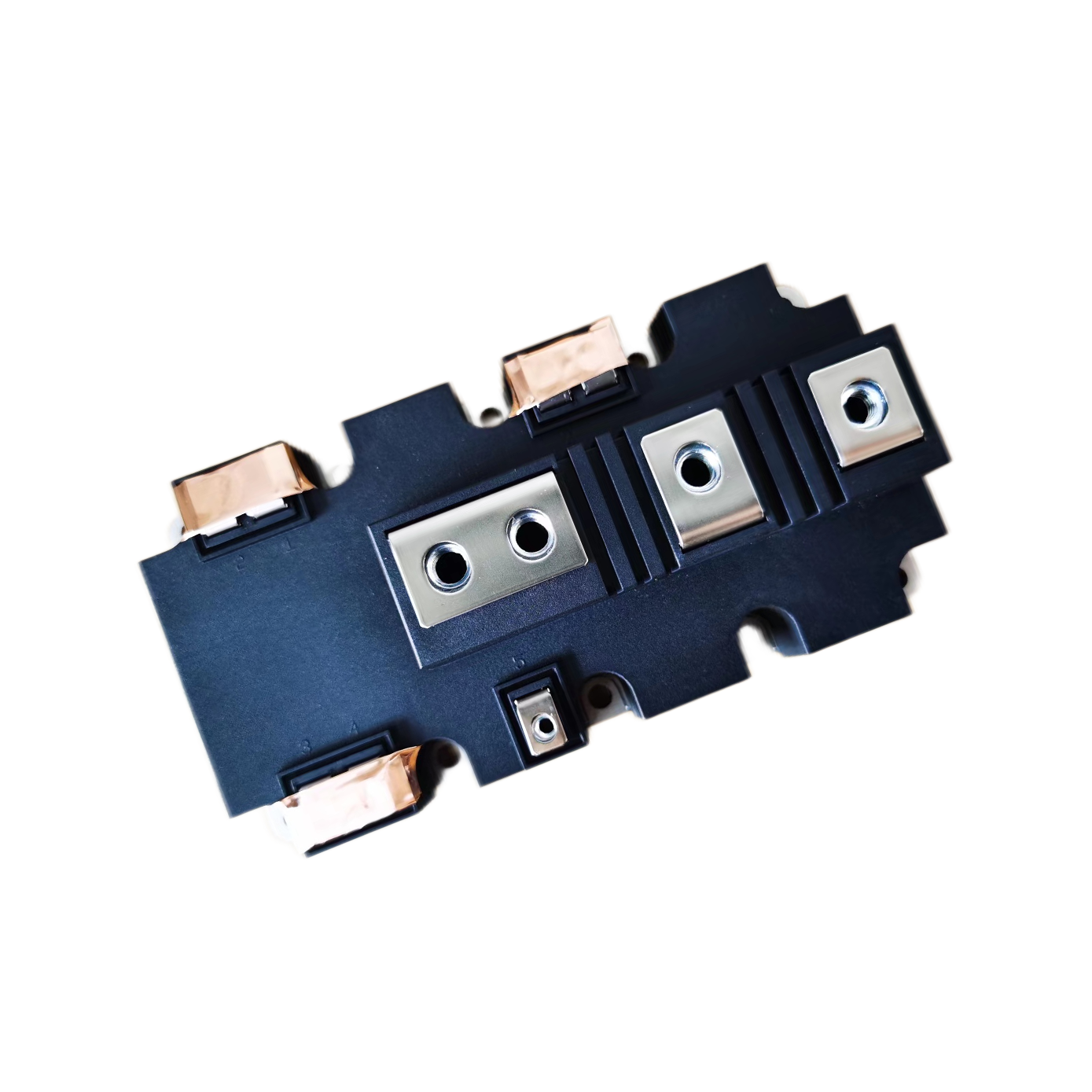
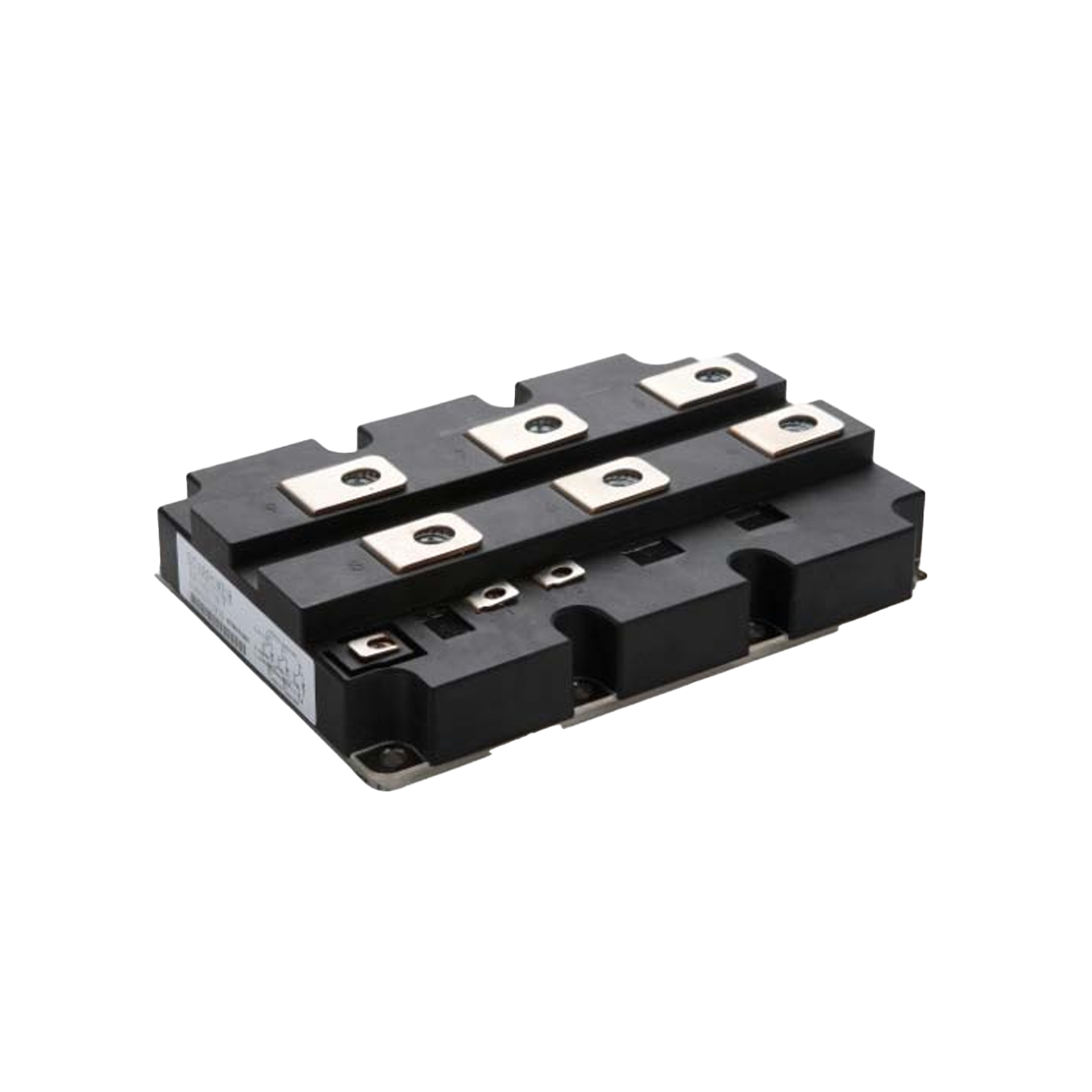
industrial thyristor
The industrial thyristor stands as a fundamental semiconductor device that revolutionizes power control and switching applications across numerous manufacturing sectors. This sophisticated electronic component functions as a controllable rectifier, enabling precise regulation of electrical power flow in heavy-duty industrial environments. The industrial thyristor operates through a four-layer PNPN structure that creates a bistable switching mechanism, allowing it to conduct current in one direction while blocking reverse current flow. When properly triggered by a gate signal, the device transitions from a blocking state to a conducting state, maintaining conduction until the current drops below a specific holding threshold. This unique operational characteristic makes the industrial thyristor exceptionally valuable for applications requiring robust power management capabilities. The technological framework of industrial thyristors incorporates advanced silicon semiconductor technology, featuring enhanced thermal management systems and superior electrical isolation properties. These devices demonstrate remarkable durability under extreme operating conditions, including high temperatures, voltage fluctuations, and electromagnetic interference commonly encountered in industrial settings. Modern industrial thyristors integrate protective features such as overcurrent protection, thermal shutdown mechanisms, and voltage surge suppression to ensure reliable long-term operation. The versatility of industrial thyristors extends across multiple application domains, including motor speed control systems, heating element regulation, lighting control circuits, and power supply management. In manufacturing facilities, these devices serve critical roles in variable frequency drives, welding equipment, electroplating systems, and automated production line controls. The industrial thyristor also finds extensive use in renewable energy systems, particularly in solar inverters and wind power conversion equipment, where efficient power conversion and grid synchronization are essential requirements.