The application of MOSFET and IGBT in charging stations
1. Introduction to Charging Stations
A charging station is a device that provides energy replenishment for electric vehicles. Its function is similar to the fueling machine in a gas station. It can be fixed on the ground or on the wall and is installed in public buildings (public buildings, shopping malls, public parking lots, etc.) and residential parking lots or charging stations. It can charge various types of electric vehicles according to different voltage levels.
The input end of the charging station is directly connected to the alternating current power grid, and the output end is equipped with a charging plug for charging the electric vehicle. Charging stations generally offer two charging methods: conventional charging and fast charging. People can use a specific charging card to swipe it on the human-machine interaction interface provided by the charging station to perform corresponding charging operations and print the fee data. The display screen of the charging station can show data such as charging quantity, fee, and charging time.
Charging stations are classified according to their charging methods: DC charging stations, AC charging stations, and AC/DC integrated charging stations.
AC charging station
An AC charging station is a power supply device that is fixedly installed outside an electric vehicle and connected to the power grid to provide an AC power source for the on-board charger of the electric vehicle (i.e., the charger fixedly installed on the electric vehicle). The AC charging station only provides power output and does not have charging functionality. It needs to be connected to the on-board charger to charge the electric vehicle, which is equivalent to merely serving as a power control function.
DC charging station
The basic components of a DC charging station include: power unit, control unit, metering unit, charging interface, power supply interface, and human-machine interaction interface, etc. The power unit refers to the DC charging module, and the control unit refers to the charging station controller. Besides these core components, a DC charging station also has some other important small parts, such as sheet metal parts, fuses, relays, and lightning protection devices, etc. As a system integration product, a DC charging station not only consists of the "DC charging module" and "charging station controller" as the technical core, but also the structural design is one of the key points in the overall reliability design of the charging station.
2. Product Application and Advantages
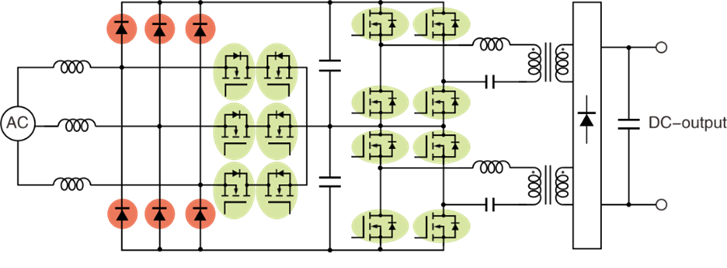
For the application in the charging station market, the high-voltage super-junction MOS of us has the following product advantages:
(1)For the LLC topology, the body diode is optimized to enhance di/dt capability, reduce Qrr and drive interference;
(2)The Vth is optimized to make the parallel operation of multiple tubes more reliable;
(3)The Qg and Coss/Ciss ratio are optimized to reduce drive loss and improve drive anti-interference ability;
(4)The EAS is optimized to enhance anti-avalanche ability.
Regarding the application in the charging station market, the product advantages of ours are:
(1)Optimizing Vceset, reducing conduction loss to a greater extent and lowering temperature rise;
(2)Optimizing the reverse parallel diode to enhance di/dt capability;
(3)Optimizing the switching speed, with the switching frequency reaching up to 60 kHz.
These advantages have made our product safer and more efficient in the application of charging stations.
3.One of the recommended products
Part Number |
LSB60R069GF |
VDS (V) |
600 |
ID (A) 25℃ |
45 |
PD (W) 25℃ |
338 |
RDS(ON) (Ω) (VGS=10V) - Typ. |
0.06186 | RDS(ON) (Ω)(VGS=10V) - Max. | 0.069 |