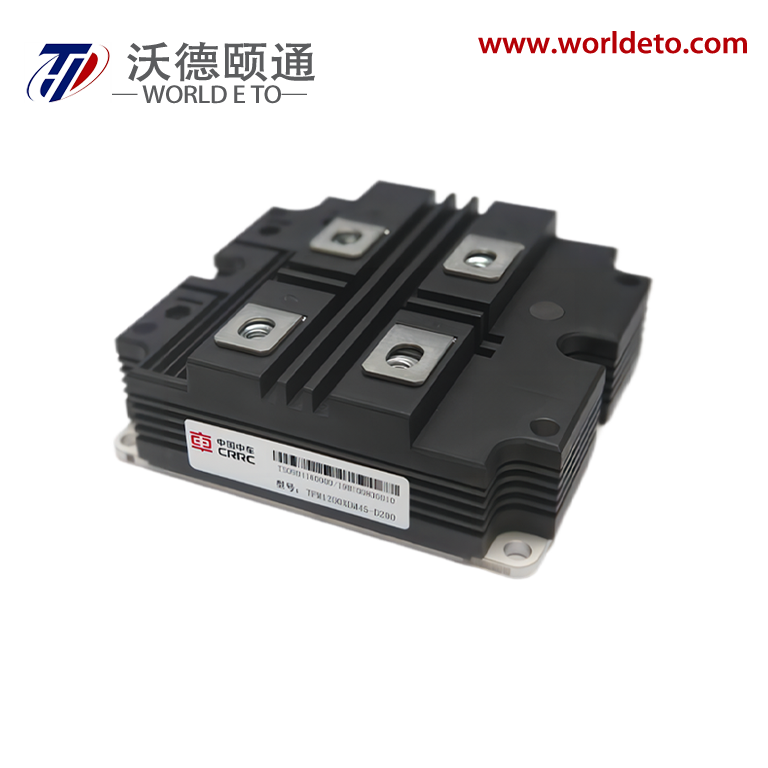
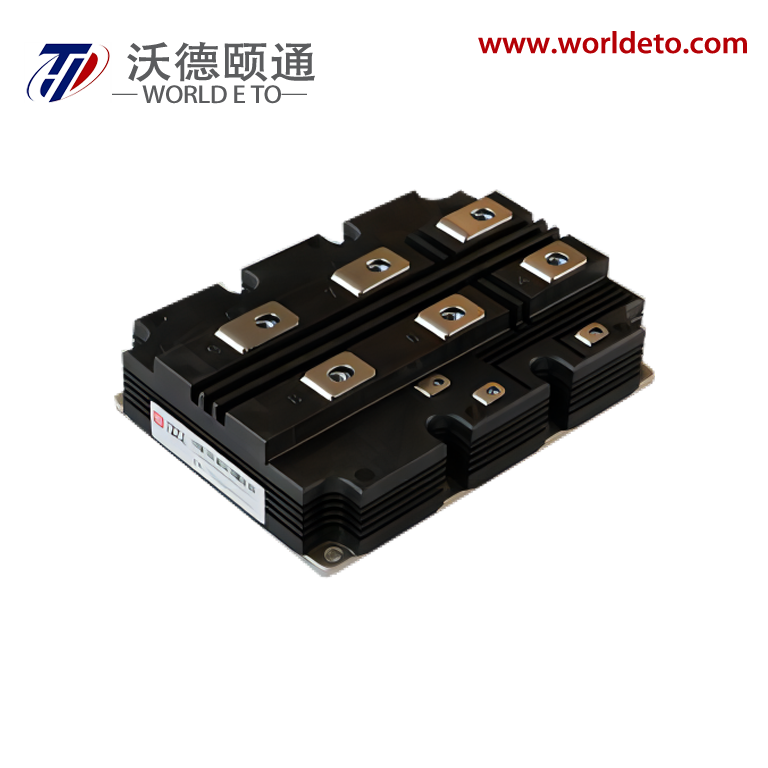
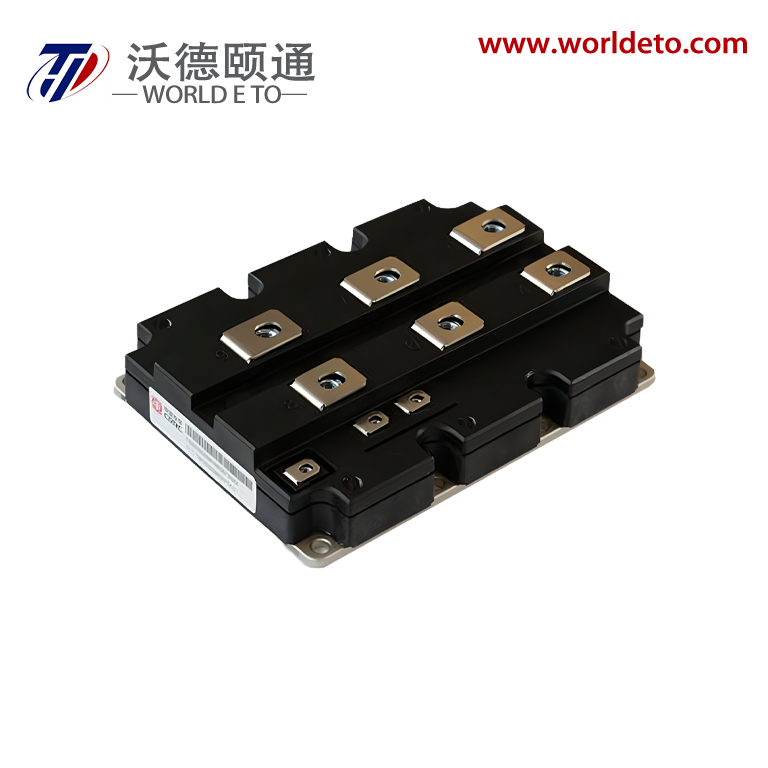
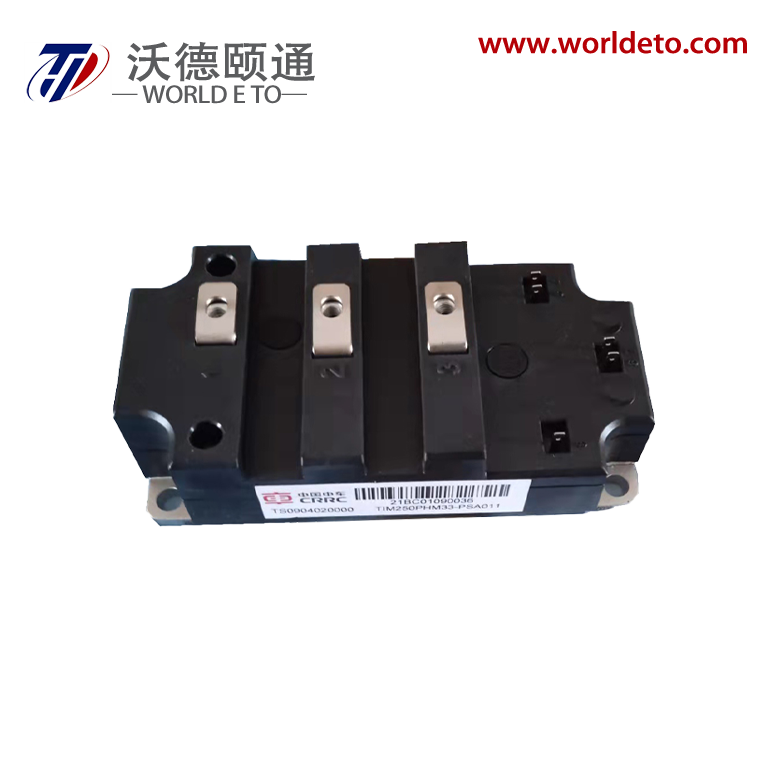
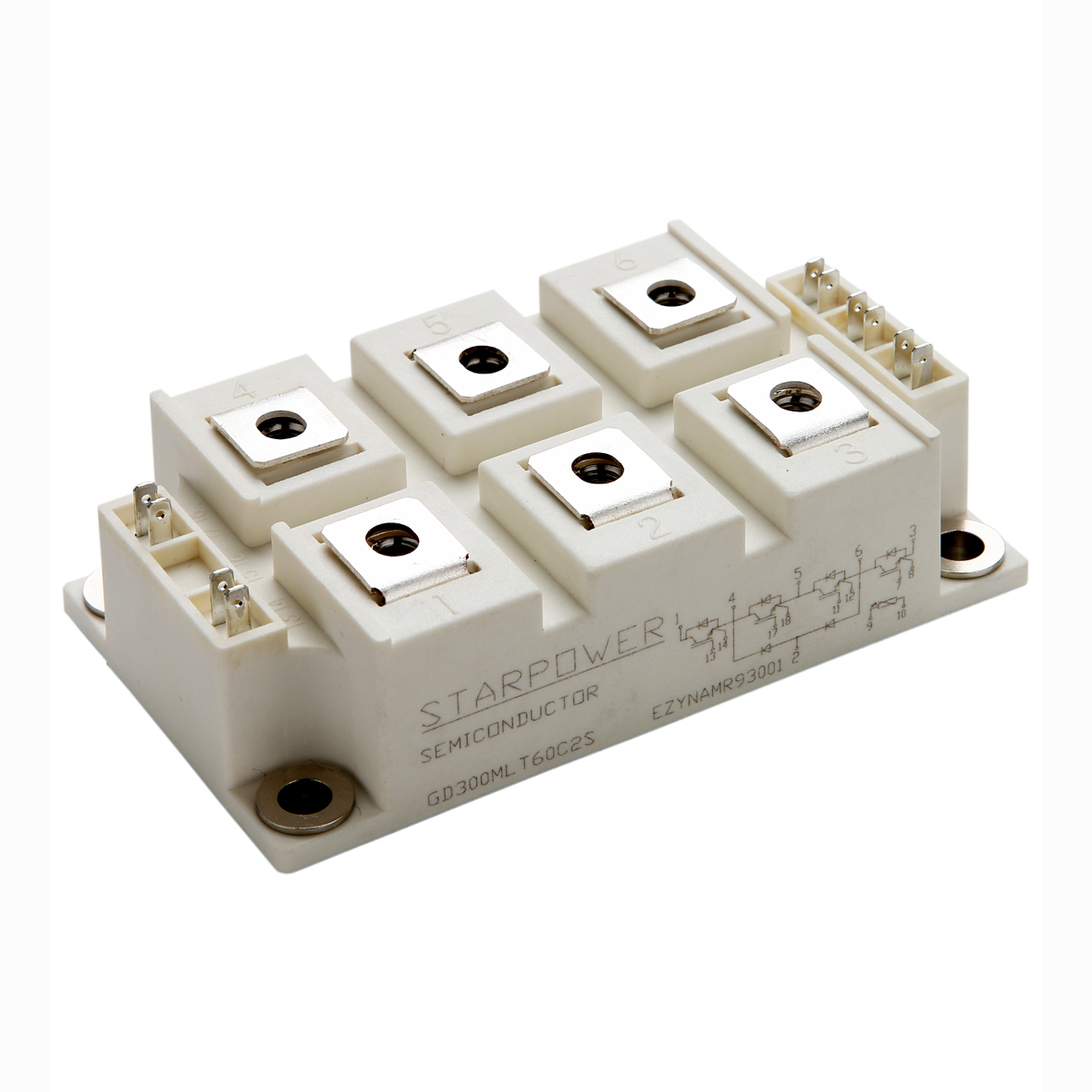
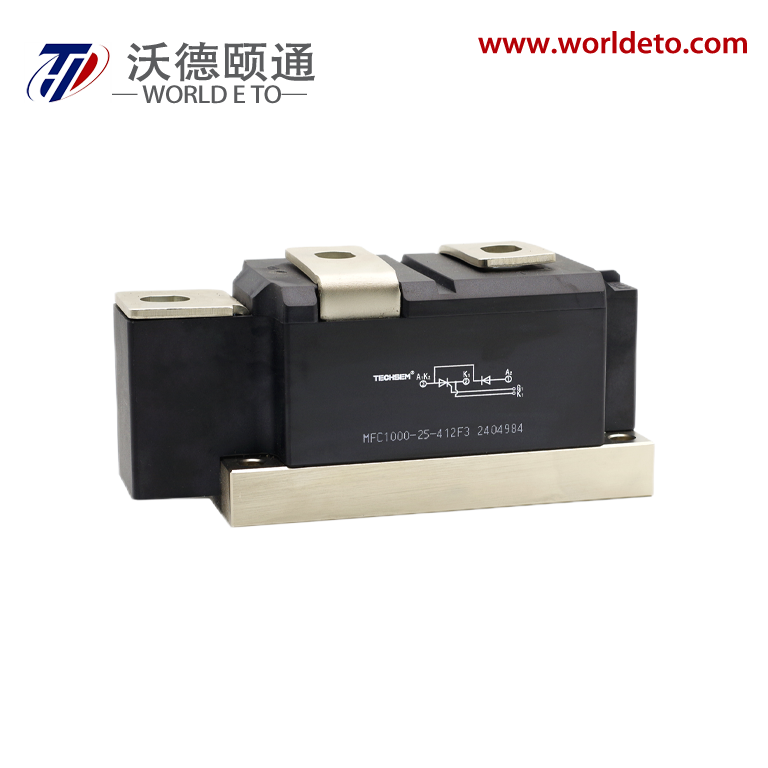
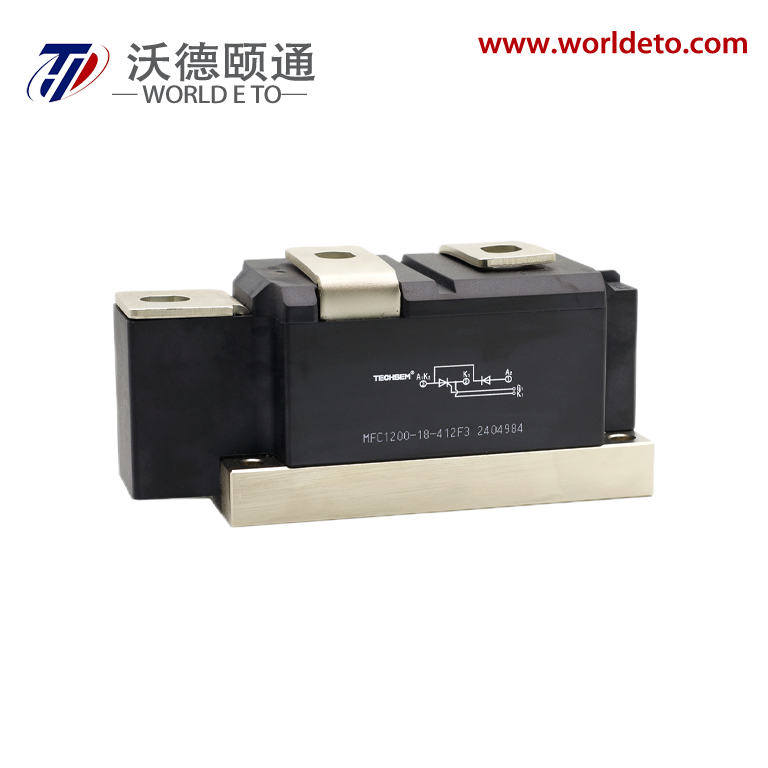
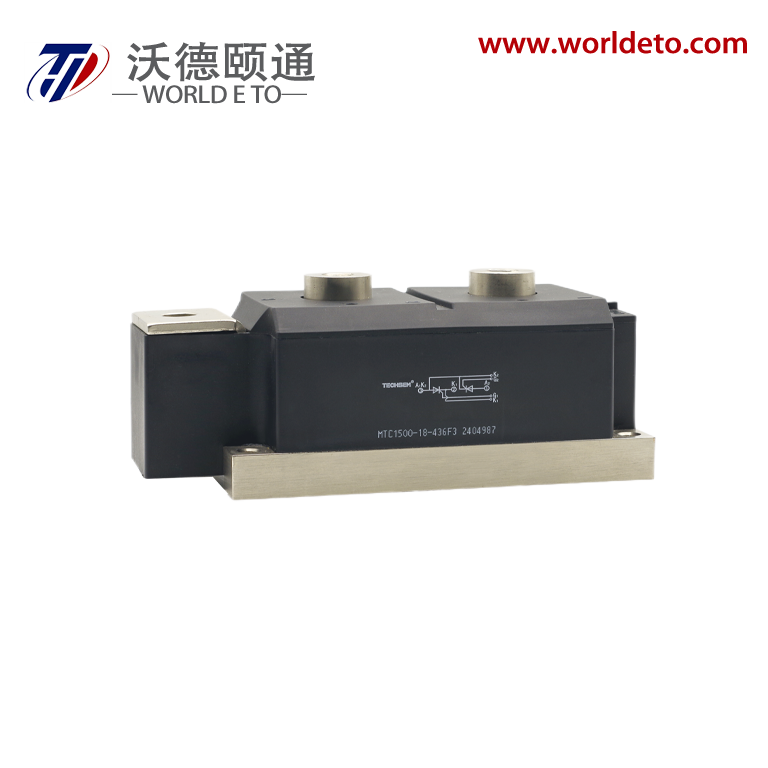
electronic transistor
The electronic transistor stands as one of the most revolutionary inventions in modern technology, fundamentally transforming how we process and control electrical signals. This semiconductor device operates as a versatile switch and amplifier, enabling the precise control of electrical current flow through three distinct terminals: the emitter, base, and collector in bipolar junction transistors, or the source, gate, and drain in field-effect transistors. The electronic transistor functions by using a small input signal to control a much larger output signal, making it an essential component in virtually every electronic device we use today. Its primary technological features include exceptional switching speeds, minimal power consumption, compact size, and remarkable durability. The device operates on the principle of semiconductor physics, where the flow of electrons and holes through specially treated silicon or germanium materials can be precisely controlled. Modern electronic transistor manufacturing employs sophisticated fabrication processes that create devices with nanometer-scale precision, allowing millions of transistors to fit on a single microchip. These components excel in digital applications where they function as binary switches, turning signals on or off with extraordinary speed and reliability. In analog applications, the electronic transistor serves as an amplifier, boosting weak signals to usable levels while maintaining signal integrity. The versatility of the electronic transistor extends across numerous industries and applications. In computing, billions of these devices work together in microprocessors and memory chips to process information at incredible speeds. Consumer electronics rely on transistors for everything from smartphone displays to audio amplification systems. Automotive systems integrate thousands of electronic transistors for engine control, safety systems, and infotainment features. Industrial equipment uses these components for motor control, automation systems, and power management. The medical field depends on transistor technology for diagnostic equipment, monitoring devices, and therapeutic instruments. Communication networks worldwide operate through sophisticated transistor-based systems that enable data transmission, signal processing, and network management. The electronic transistor continues to evolve with advancing technology, incorporating new materials and design innovations that push the boundaries of performance and efficiency.