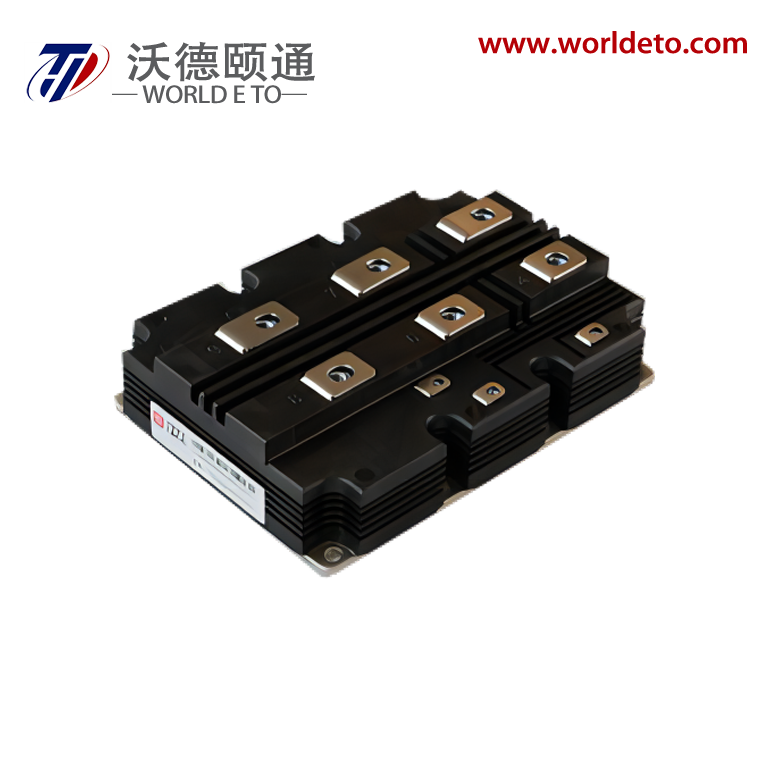
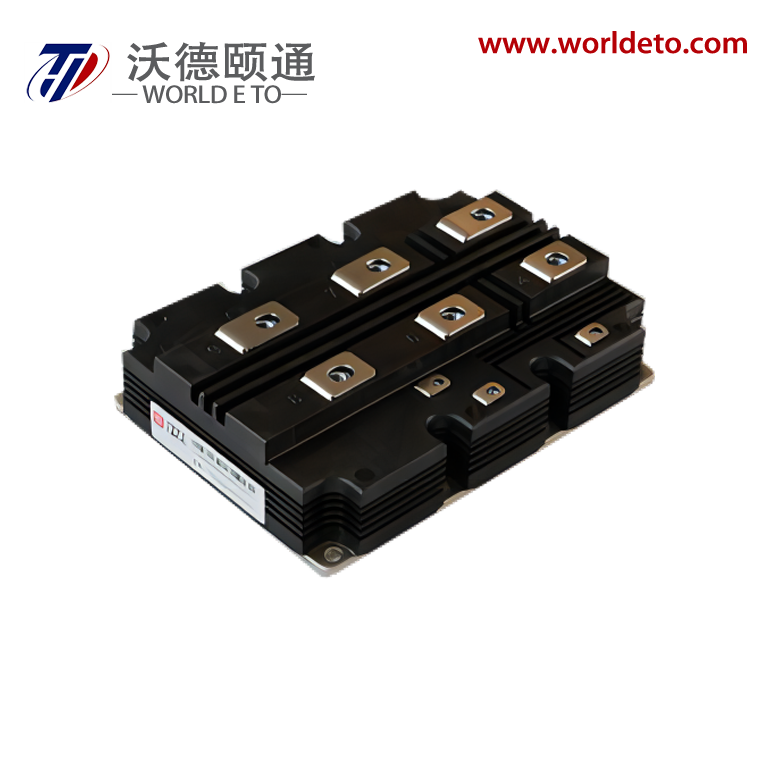
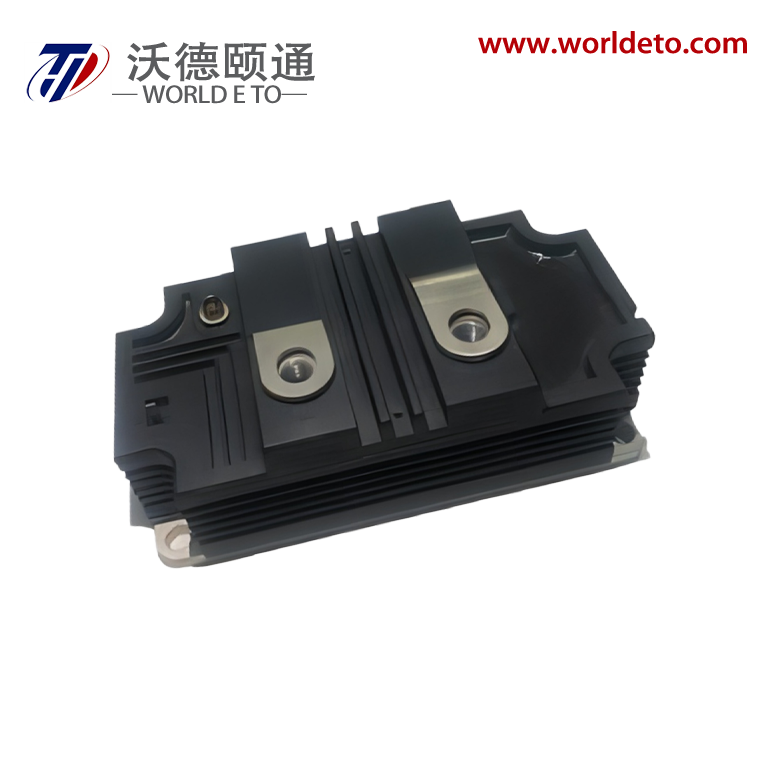
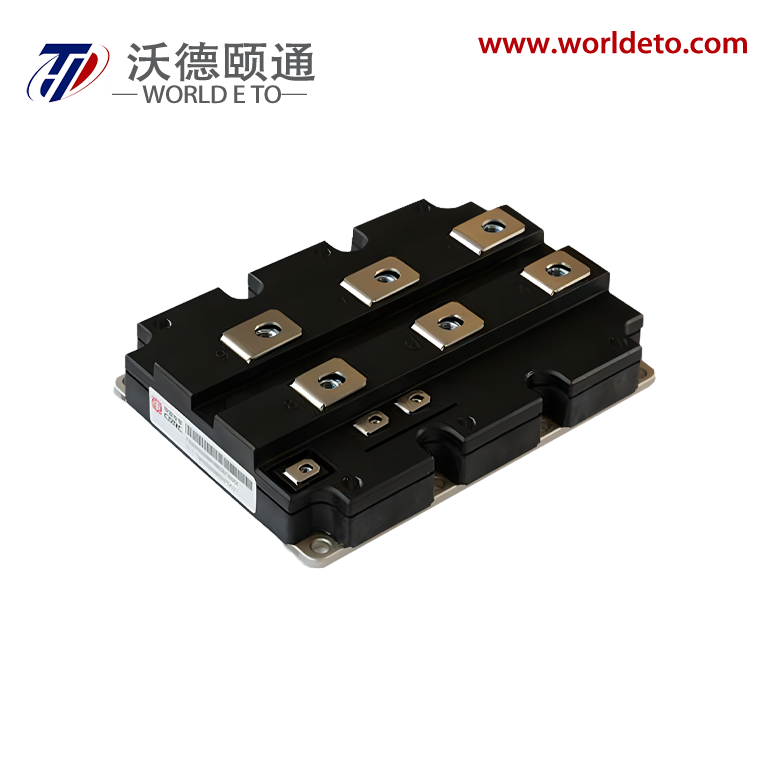
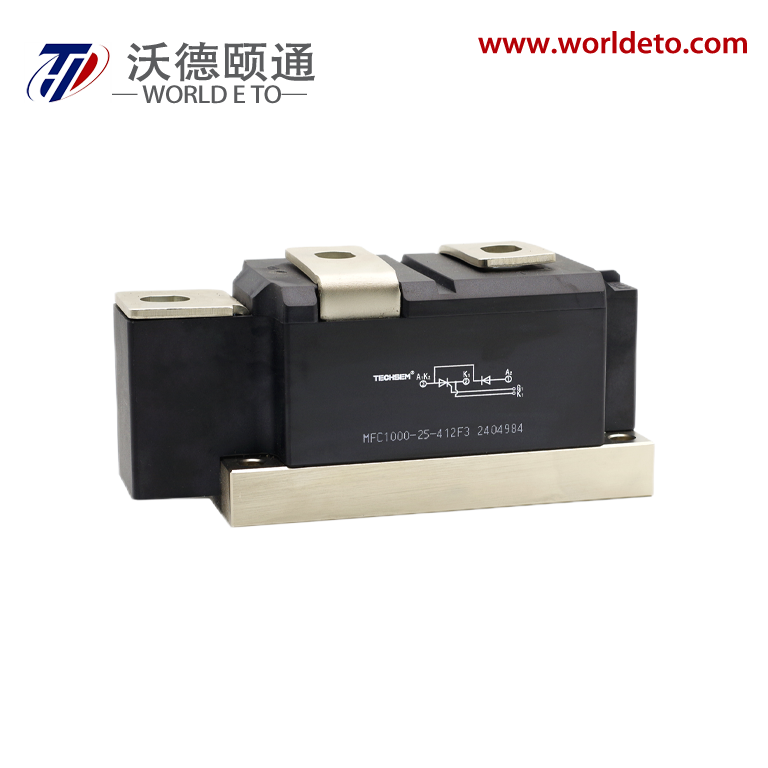
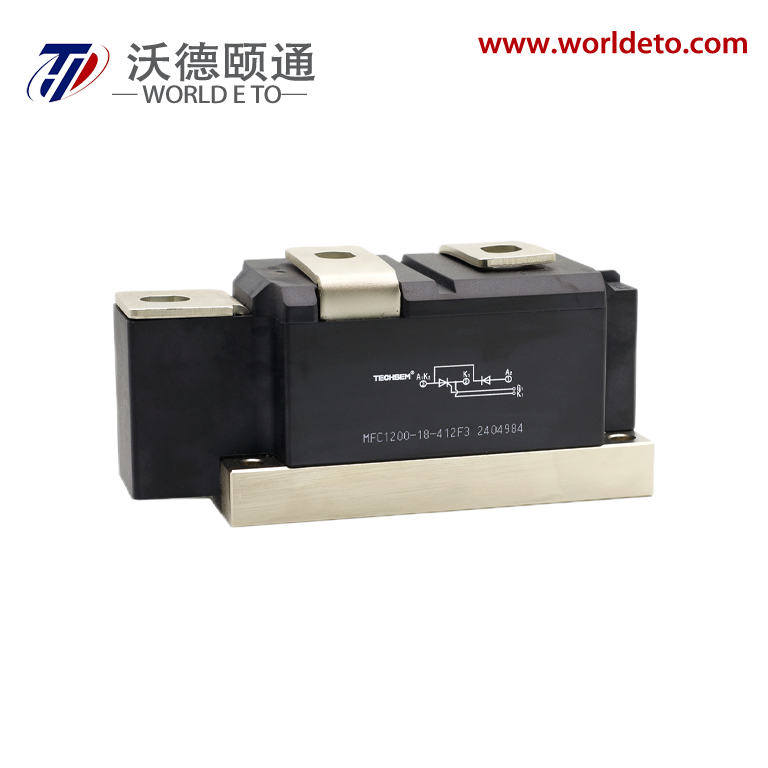
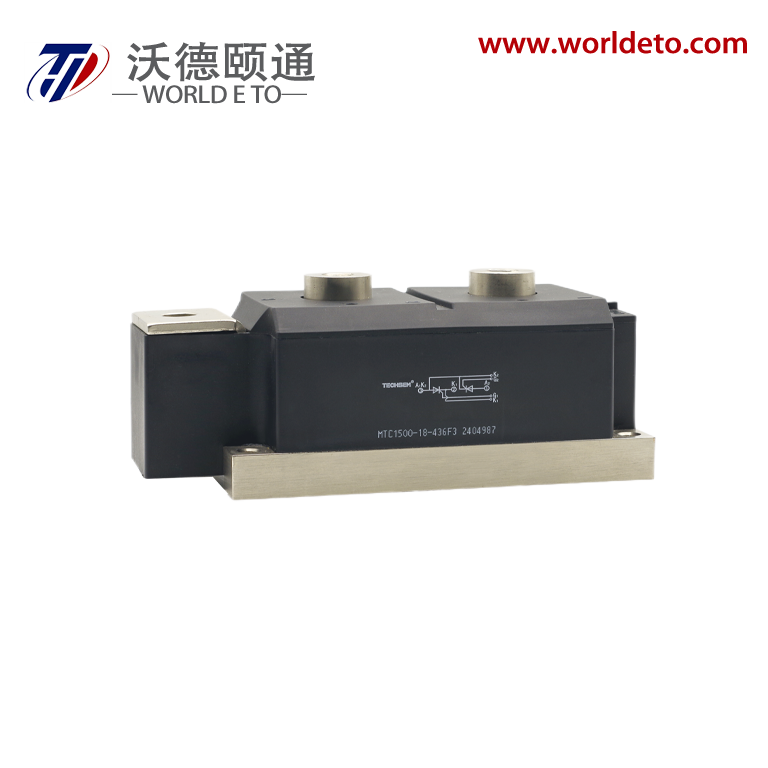
inverter transistor
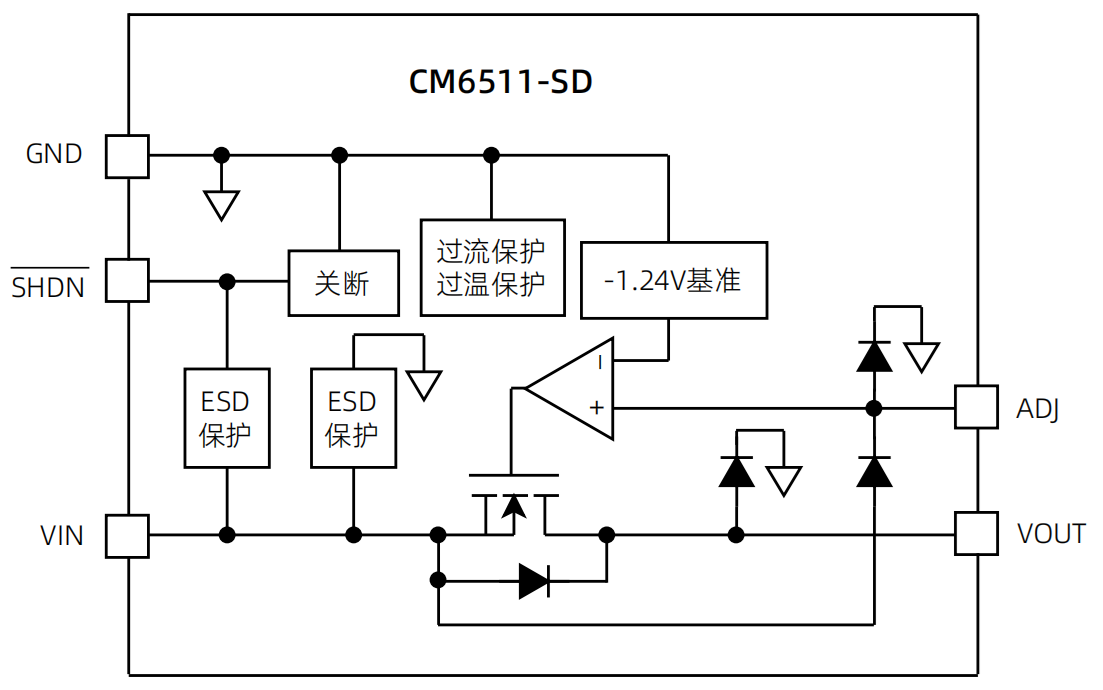
An inverter transistor represents a fundamental building block in modern power electronics and digital switching applications. This specialized semiconductor device serves as the cornerstone for converting direct current (DC) electrical power into alternating current (AC) power through sophisticated switching operations. The inverter transistor operates by rapidly switching between on and off states, creating the necessary waveforms to produce AC output from DC input sources. These devices integrate advanced semiconductor materials and precise engineering to deliver reliable performance across diverse operating conditions. The primary function of an inverter transistor involves controlling electrical current flow through strategic gate control mechanisms. When voltage signals activate the gate terminal, the transistor switches to its conductive state, allowing current to pass through the device. Conversely, removing the gate signal switches the transistor to its non-conductive state, blocking current flow. This fundamental switching capability enables the creation of complex waveforms required for AC power generation. Modern inverter transistors incorporate sophisticated technological features that enhance their operational capabilities. These include improved thermal management systems that dissipate heat effectively during high-power operations. Advanced packaging technologies protect the semiconductor junction from environmental factors while maintaining optimal electrical performance. The devices feature low on-resistance characteristics that minimize power losses during conduction phases. Fast switching speeds enable high-frequency operations essential for modern power conversion systems. Contemporary inverter transistors utilize materials like silicon carbide and gallium nitride that offer superior electrical properties compared to traditional silicon designs. These wide bandgap semiconductors provide enhanced efficiency, reduced switching losses, and improved thermal performance. The devices incorporate intelligent protection features that prevent damage from overcurrent conditions, excessive temperatures, and voltage spikes. Applications for inverter transistors span numerous industries and technological sectors. Solar power systems rely on these devices to convert DC energy from photovoltaic panels into AC electricity compatible with electrical grids. Electric vehicle charging stations use inverter transistors to manage power conversion between different voltage levels and current types. Industrial motor drives incorporate these components to control speed and torque in manufacturing equipment. Consumer electronics utilize miniaturized versions for power management in laptops, smartphones, and household appliances.