price of thyristor
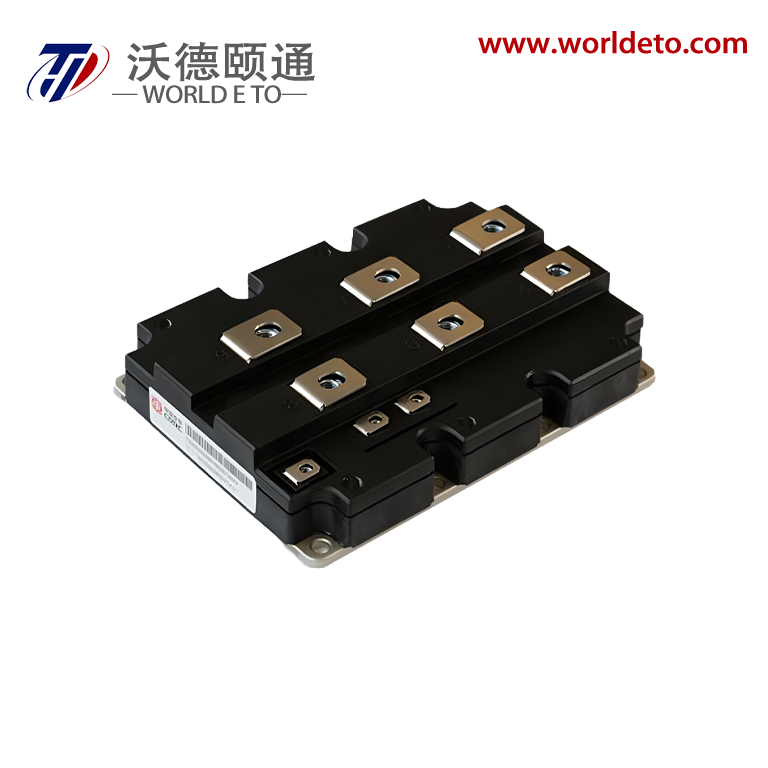
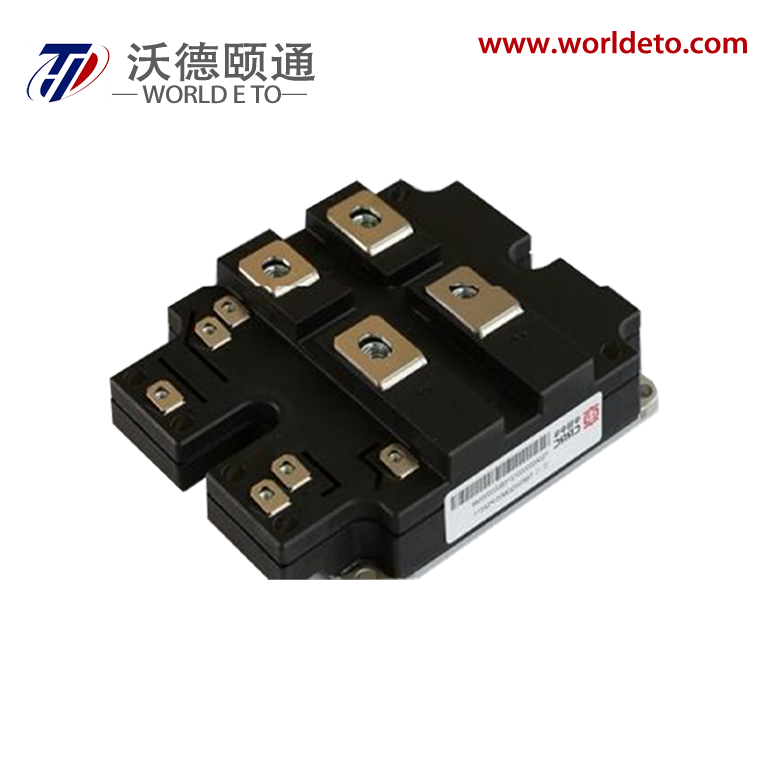
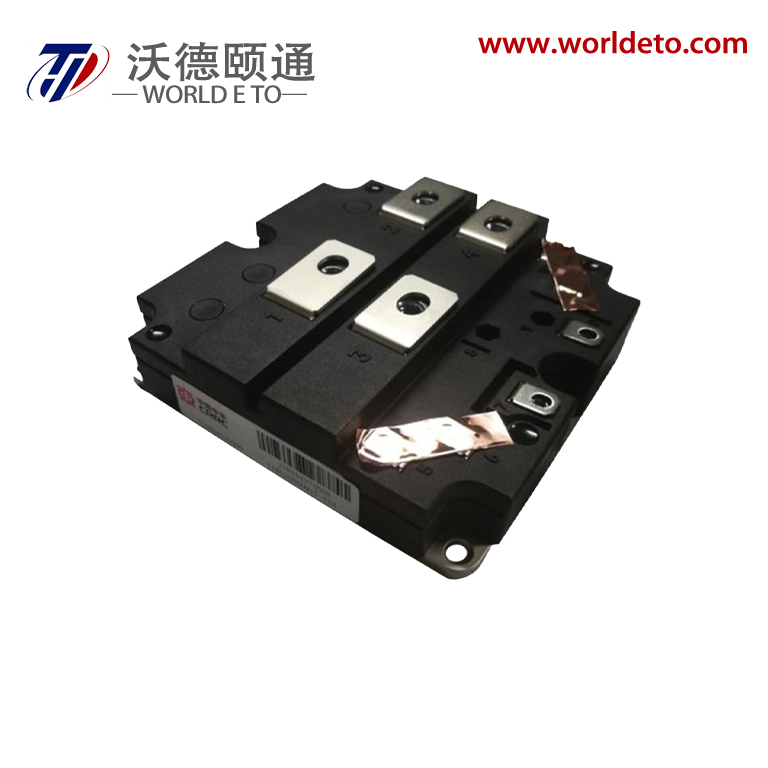
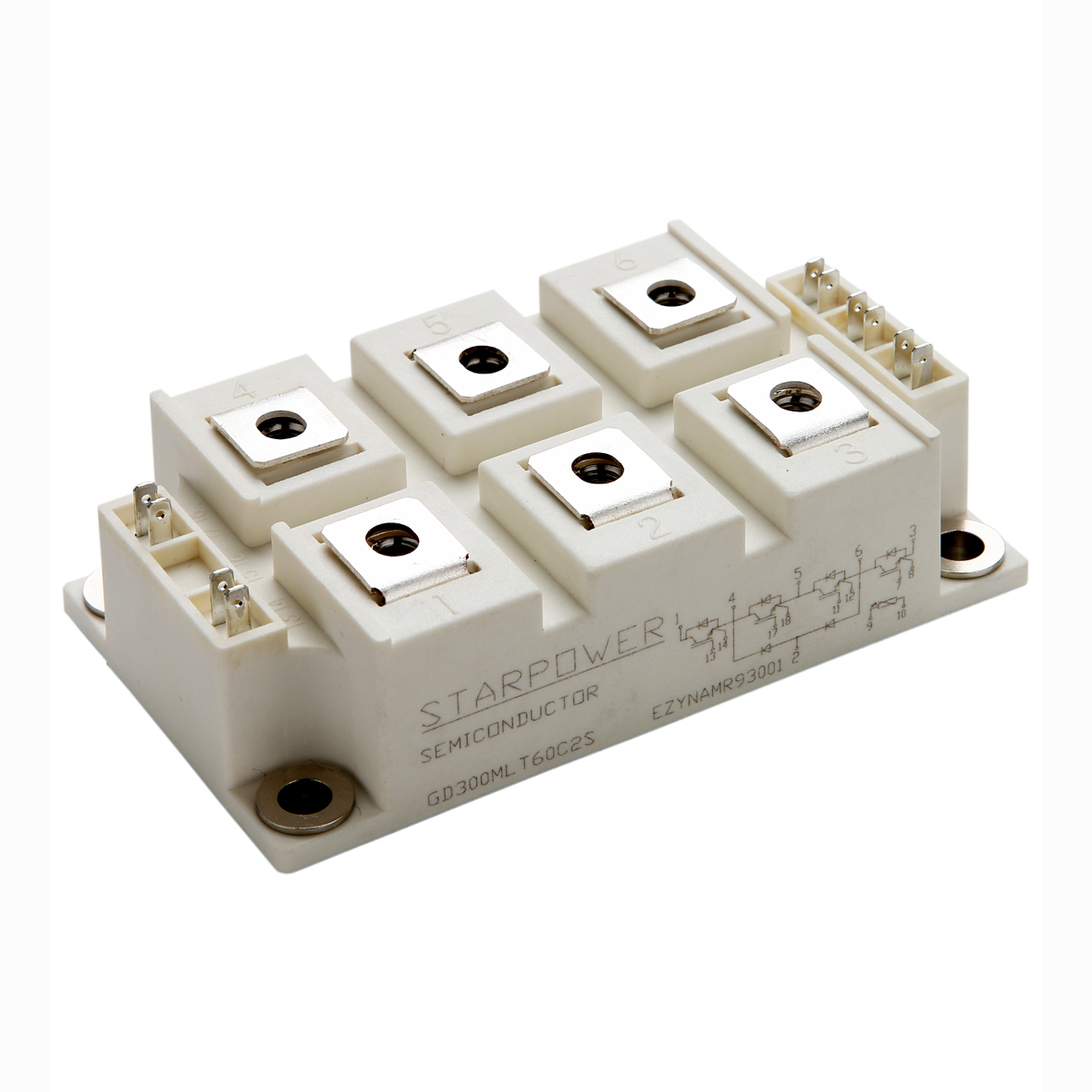
Understanding the price of thyristor components requires examining their essential functions and technological capabilities in modern electronic systems. Thyristors serve as semiconductor switching devices that control electrical current flow in high-power applications, making them indispensable for industrial automation and power management solutions. These devices operate by switching between conducting and non-conducting states, enabling precise control over electrical circuits while handling substantial voltage and current levels. The price of thyristor units reflects their sophisticated silicon-controlled rectifier technology, which incorporates four-layer PNPN semiconductor structures for reliable performance. Manufacturing costs influence the price of thyristor devices through advanced fabrication processes that ensure consistent switching characteristics and thermal stability. Gate-controlled operation allows thyristors to remain in conducting states once triggered, eliminating the need for continuous control signals and reducing overall system complexity. Power electronics applications extensively utilize thyristors for motor drives, welding equipment, lighting controls, and renewable energy systems where efficient switching capabilities are paramount. The price of thyristor components varies based on current ratings, voltage specifications, and package configurations that meet specific application requirements. Silicon carbide variants command higher prices due to superior thermal performance and reduced switching losses compared to traditional silicon designs. Temperature coefficients and surge current handling capabilities directly impact the price of thyristor selections for demanding industrial environments. Triggering sensitivity and holding current specifications determine suitability for different circuit designs, influencing both performance outcomes and cost considerations. Market dynamics affect the price of thyristor inventory through supply chain factors, manufacturing capacity, and technological advancement cycles that drive innovation in semiconductor switching technology.